背景介绍:当我们在从事大项目或团队开发工作时,我们经常会发现我们写的代码,凌乱、难以阅读并且难以扩展。尤其是当一段时候后我们回头再看自己的代码,必须回想起当初自己写的时候的思路才能看懂。
因此,人们尝试在代码风格上保持统一,然而,最大的困难是:修改一个较小的问题,都可能创建更多丑陋的 hack,也可能 CSS 的小改变会影响 JavaScript 的功能。但是这些问题能在我们的项目开始的时候精心规划,就能很大程度上避免这些问题。今天就来讨论一下如何写一份不错的CSS代码
一个好的css代码是什么样的呢
- 保持样式表可维护
- 保持代码可读性
- 保持样式表的可扩展性
要保持良好的CSS代码,首先需要订立一致的CSS团队规范,这就必须从CSS架构讲起。
CSS架构
目前CSS主要有以下五种设计架构
1. OOCSS
面向对象的CSS,
- 结构和主题分离 - 减少对 HTML 结构的依赖
- 主题和主题分离 - 增加样式的复用性
在OOCSS的基础上,出现了另一种设计模式
2. BEM
也可以被当成一种命名规范,本质上使页面结构清晰
块(Block)、元素(Element__)、修饰符(Modifier--)
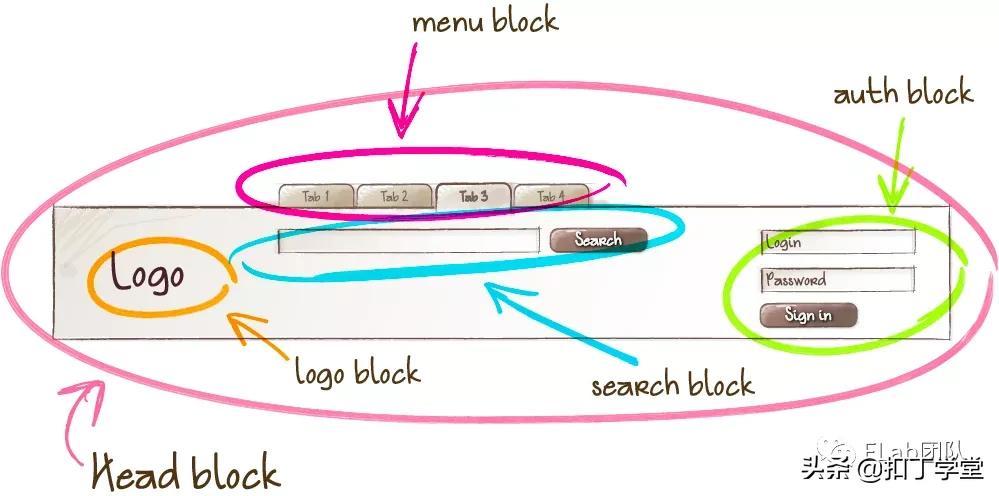
有以下几个规则
- Block元素应该以元素本身的属性为主
- Element则以元素位置和形状为主
- Modifier则修饰当前的状态和主题
- Element一定是在Block之中,而不能独立于Block之外
- Modifier则更多的表示当前组件的形状和状态
可以明显发现
- 结构清晰
- 定位迅速
- 功能明确
在面对组件化的场景时,Block 代表逻辑上和功能上独立的页面组件。Element封装了行为(JavaScript)、模板、样式(CSS)和其他实现技术。
举个例子
<header class="header"> <img class="logo"> <form class="search-form"> <input class="input"> <button class="button"></button> </form> <ul class="lang-switcher"> <li class="lang-switcher__item"> <a class="lang-switcher__link" href="url">en</a> </li> <li class="lang-switcher__item"> <a class="lang-switcher__link--active" href="url">ru</a> </li> </ul></header>- block-name__element-name--modifier-name--modifier-value
在React当中,也采用了这样的命名方式
BEMnaming工具[1],提供BEM命名的检测
然而在面对大型的项目时CSS的凌乱也很难让开发者愿意在茫茫多的代码中寻找可复用的代码
3. SMACSS
(What’s Smacss)[https://smacss.com/]
设计的主要规范有三点:
- Categorizing CSS Rules(为css分类)
- Naming Rules(命名规范)
- Minimizing the Depth of Applicability(最小化适配深度)
为了实现清晰的CSS结构,将CSS分为
- Base - 全局样式,如global-reset、normalize.css
- Layout - 页面布局,如grid
- Module - 组件布局
- State - 元素状态,如visible、hidden
- Theme or Skin - 更多是具体主题的配置样式
- JavaScript 勾子 (JavaScript hooks)
其中尤其建议JavaScript解除和样式的耦合
<button class="btn btn--buy js-buy-now"></button>命名规范上出现了一些差异
.layout-header.is-hidden.theme-nav最小化适配深度,减少html和css的耦合度,避免html的变动增加对css的影响
.sidebar ul h3 {}.side {}4. ITCSS
对CSS进行了更加详细的分层

如果从功能的角度上看呢,是将Base分成了Settings、Tools、Generic和Base,而Objects、Components和Trumps则分别对应Layout、Module、(State、Theme),而这样设计的好处在于可以将代码的复用性进一步提升
5. ACSS
一个样式属性一个类,其中的典型代表就是TailwindCSS[2],缺点则是破坏了语义化
.block{ display: block; }.hidden { display: none; }.p-2 { padding: 0.75rem; }.flex { display: flex; }.text-base { font-size: 1rem; }.bg-green-200 { background-color: #123456 }<div className="m-2 p-2 text-2xl text-gray-500">I am Ok</div>而上述的架构思想,更多则是需要团队成员的一致性认同,才能实现在代码风格上的统一。
除了这些开发自律性上的代码规范外,还有什么其他的方式来提升CSS质量呢?
CSS预处理器
在预处理器中,同样提供了众多的方法来简化与控制CSS代码,以stylus为例
1. 变量
font-size = 14px body font font-size Arial, sans-serif pad(types = padding, n = 5px) if padding in types padding n if margin in types margin nbody pad()body pad(margin)body pad(padding margin, 10px) // Yields:body { padding: 5px;}body { margin: 5px;}body { padding: 10px; margin: 10px;}2. 函数
add(a, b = a) a + b add(10, 5) // => 15 get(hash, key) return pair[1] if pair[0] == key for pair in hash hash = (one 1) (two 2) (three 3) get(hash, two) // => 2 get(hash, three) // => 3 get(hash, something) // => null3. 内建函数
// 提取颜色分量red(#c00)// => 204red(#000, 255)// => #f004. 插值
// 属性插值vendor(prop, args) -webkit-{prop} args -moz-{prop} args {prop} argsborder-radius() vendor('border-radius', arguments)box-shadow() vendor('box-shadow', arguments)button border-radius 1px 2px / 3px 4px // Yields: button { -webkit-border-radius: 1px 2px / 3px 4px; -moz-border-radius: 1px 2px / 3px 4px; border-radius: 1px 2px / 3px 4px; } // 选择器插值 table for row in 1 2 3 4 5 tr:nth-child({row}) height: 10px * row // Yields: table tr:nth-child(1) { height: 10px;}table tr:nth-child(2) { height: 20px;}table tr:nth-child(3) { height: 30px;}table tr:nth-child(4) { height: 40px;}table tr:nth-child(5) { height: 50px;} mySelectors = '#foo,#bar,.baz'{mySelectors} background: #000 Yields:#foo,#bar,.baz { background: #000;} // 对象插值foo = { width: 10px, height: 20px, '&:hover': { padding: 0 }}.bar {foo}Yields:// => .bar {// width: 10px;// height: 20px;// }// .bar:hover {// padding: 0;// }5. @EXTEND
form input[type=text] padding: 5px border: 1px solid #eee color: #ddd textarea @extends form input[type=text] padding: 10px //Yielding: form input[type=text], textarea { padding: 5px; border: 1px solid #eee; color: #ddd; } textarea { padding: 10px; }对于维护一份高质量的CSS代码,注释和间隔必不可少
以下是一种比较建议的注释和间隔方式,可以自行取用。
/*------------------------------------*\ #A-SECTION*------------------------------------*/.selector { }/*------------------------------------*\ #ANOTHER-SECTION*------------------------------------*//** * Comment */.another-selector { }除了缩进,我们还可以通过在规则集之间自由而明智地使用空格来提供大量信息。我们用:
- 密切相关的规则集之间的一 (1) 条空行。
- 松散相关的规则集之间的两 (2) 条空行。
- 全新部分之间的五 (5) 行空行。
// good case/*------------------------------------*\ #FOO*------------------------------------*/.foo { } .foo__bar { }.foo--baz { }// bad case.foo { } .foo__bar { }.foo--baz { }同理,在html结构中,也可以使用同样的规则。
除了以上这些,还有众多的规范和优化可以继续探索,如选择器性能,CSS嵌套,有兴趣的读者可以继续探索
你会认为 CSS规范是一个有点宏大和不必要的概念:为什么这么简单、这么直接的东西需要像架构一样被设计成非常复杂的东西?!
正是因为CSS 的简单性、松散性和不守规矩的性质意味着在任何合理规模上管理(阅读、驯服)它的最佳方式是通过严格和特定的架构。坚实的架构可以帮助我们控制我们的特殊性,强制执行命名约定,管理我们的源代码顺序,创建一个健全的开发环境,并且通常使我们的 CSS 项目管理更加一致和舒适。
总的来说,可以依照一下几个规则订立团队/个人代码规范,保证代码的一致性
建议的几个原则
单一职责原则: 每个 CSS 实现都必须有一个单一的责任。
Correct: .button { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; border: 1px solid black; background: #fff; } .header__button { margin: 30px; position: relative; } Incorrect: .header__button { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; position: relative; border: 1px solid black; margin: 30px; }开闭原则: 元素应该通过修饰符扩展,而不是直接在原有基础上修改。
Original: <button class="button">...</button> .button { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; text-align: center; font-size: 11px; line-height: 20px; } Extend <button class="button button_size_s">...</button> .button { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; text-align: center; font-size: 11px; line-height: 20px; } .button_size_s { font-size: 13px; line-height: 24px; }DRY原则:将有意义的重复规范化和抽象化
巧用mixin和extend@mixin my-web-font() { font-family: "My Web Font", sans-serif; font-weight: bold;}.btn { display: inline-block; padding: 1em 2em; @include my-web-font();}.foo { color: red;}.bar { @extend .foo;}组合优于继承和关注点分离
// 将写js的方式同样适用在css上<div class="layout"> <div class="layout__item two-thirds"> <section class="content"> ... </section> </div> <div class="layout__item one-third"> <section class="sub-content"> ... </section> </div></div>参考文献
BEM简介[3]
OOCSS介绍[4]
探索 SMACSS:可扩展的模块化 CSS 框架[5]
编写高效的 CSS 选择器[6]
CSS的单一原则[7]
思考CSS架构[8]
参考资料
[1]BEMnaming工具:
https://github.com/bem/bem-sdk#naming
[2]TailwindCSS: https://www.tailwindcss.cn/
[3]BEM简介:
https://en.bem.info/methodology/quick-start/
[4]OOCSS介绍: http://oocss.org/
[5]探索 SMACSS:可扩展的模块化 CSS 框架:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/44851489
[6]编写高效的 CSS 选择器:
https://csswizardry.com/2011/09/writing-efficient-css-selectors/
[7]CSS的单一原则:
https://csswizardry.com/2012/04/the-single-responsibility-principle-applied-to-css/
[8]思考CSS架构:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/32952130
 鲁公网安备37020202000738号
鲁公网安备37020202000738号