Redis分布式锁:10分钟掌握核心技巧
发表时间: 2021-09-22 10:40
道阻且长,行则将至。请相信我,你一定会更优秀!




public static void doSomething() {// RedisLock是我封装的一个类,后面会讲到RedisLock redisLock = new RedisLock(jedis); // 创建jedis实例的代码省略,不是重点try {redisLock.lock(); // 上锁// 处理业务System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 线程处理业务逻辑中...");Thread.sleep(2000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 线程处理业务逻辑完毕");redisLock.unlock(); // 释放锁} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
public static void doSomething() {RedisLock redisLock = new RedisLock(jedis); // 创建jedis实例的代码省略,不是重点try {redisLock.lock(); // 上锁,必须在 try{}中// 处理业务System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 线程处理业务逻辑中...");Thread.sleep(2000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 线程处理业务逻辑完毕");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {redisLock.unlock(); // 在finally{} 中释放锁}}
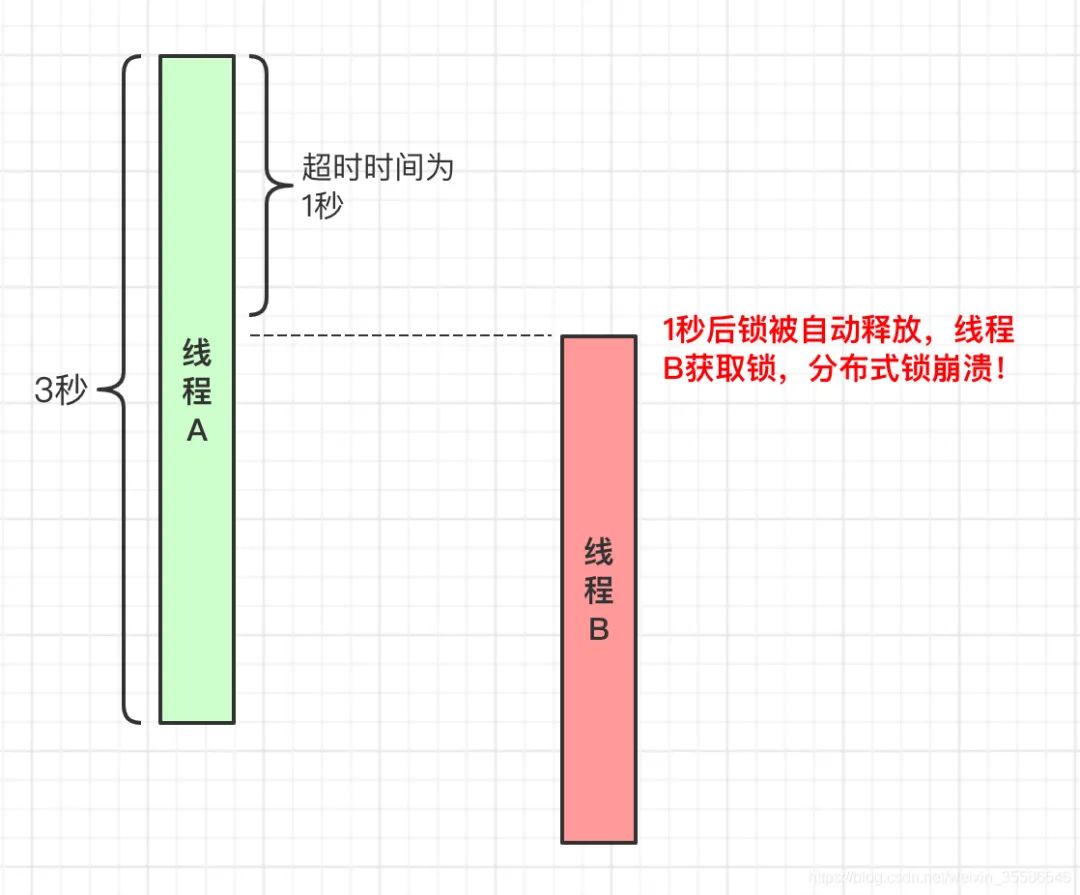
public static final String lock_key = "haolin-lock";public void lock() {while (!tryLock()) {try {Thread.sleep(50); // 在while中自旋,如果说读者想设置一些自旋次数,等待最大时长等自己去扩展,不是此处的重点} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println("线程:" + threadName + ",占锁成功!★★★");}private boolean tryLock() {SetParams setParams = new SetParams();setParams.ex(1); // 超时时间1ssetParams.nx(); // nxString response = jedis.set(lock_key, "", setParams); // 转换为redis命令就是:set haolin-key "" ex 1 nxreturn "OK".equals(response);}
// http://redis.io/commands/set.htmlSET key value [EX seconds] [PX milliseconds] [NX|XX]
set k vexipre k timeprivate boolean tryLock() {SetParams setParams = new SetParams();setParams.ex(1); // 超时时间1ssetParams.nx(); // nxString response = jedis.set(lock_key, "", setParams); // 转换为redis命令就是:set haolin-key "" ex 1 nxreturn "OK".equals(response);}// 别的线程直接调用释放锁操作,分布式锁崩溃!public void unlock() {jedis.del(encode(lock_key));System.out.println("线程:" + threadName + " 释放锁成功!☆☆☆");}private byte[] encode(String param) {return param.getBytes();}
String releaseLock_lua = "if redis.call(\"get\",KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] \n" +"then\n" +" return redis.call(\"del\", KEYS[1])\n" +"else\n" +" return 0\n" +"end";private boolean tryLock(String uuid) {SetParams setParams = new SetParams();setParams.ex(1); // 超时时间1ssetParams.nx(); // nxString response = jedis.set(lock_key, uuid, setParams); // 转换为redis命令就是:set haolin-key "" ex 1 nxreturn "OK".equals(response);}public void unlock(String uuid) {List<byte[]> keys = Arrays.asList(encode(lock_key));List<byte[]> args = Arrays.asList(encode(uuid));// 使用lua脚本,保证原子性long eval = (Long) jedis.eval(encode(releaseLock_lua), keys, args);if (eval == 1) {System.out.println("线程:" + threadName + " 释放锁成功!☆☆☆");} else {System.out.println("线程:" + threadName + " 释放锁失败!该线程未持有锁!!!");}}private byte[] encode(String param) {return param.getBytes();}
get k // 进行秘钥 value的比对del k // 比对成功后,删除k
String releaseLock_lua = "if redis.call(\"get\",KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] \n" +"then\n" +" return redis.call(\"del\", KEYS[1])\n" +"else\n" +" return 0\n" +"end";String addLockLife_lua = "if redis.call(\"exists\", KEYS[1]) == 1\n" +"then\n" +" return redis.call(\"expire\", KEYS[1], ARGV[1])\n" +"else\n" +" return 0\n" +"end";public void lock() {// 判断是否可重入if (isHeldByCurrentThread()) {return;}while (!tryLock()) {try {Thread.sleep(50); // 自旋} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println("线程:" + threadName + ",占锁成功!★★★");}// 是否是当前线程占有锁,同时将超时时间重新设置,这个很重要,同样也是原子操作private boolean isHeldByCurrentThread() {List<byte[]> keys = Arrays.asList(encode(lock_key));List<byte[]> args = Arrays.asList(encode(String.valueOf(threadId)), encode(String.valueOf(1)));long eval = (Long) jedis.eval(encode(addLockLife_lua), keys, args);return eval == 1;}private boolean tryLock(String uuid) {SetParams setParams = new SetParams();setParams.ex(1); // 超时时间1ssetParams.nx(); // nxString response = jedis.set(lock_key, String.valueOf(threadId), setParams); // 转换为redis命令就是:set haolin-key xxx ex 1 nxreturn "OK".equals(response);}public void unlock(String uuid) {List<byte[]> keys = Arrays.asList(encode(lock_key));List<byte[]> args = Arrays.asList(encode(String.valueOf(threadId)));// 使用lua脚本,保证原子性long eval = (Long) jedis.eval(encode(releaseLock_lua), keys, args);if (eval == 1) {System.out.println("线程:" + threadName + " 释放锁成功!☆☆☆");} else {System.out.println("线程:" + threadName + " 释放锁失败!该线程未持有锁!!!");}}private byte[] encode(String param) {return param.getBytes();}
// static变量,final修饰,加载在内存中,JVM进程生命周期中不变private static final String APP_ID = UUID.randomUUID().toString();String releaseLock_lua = "if redis.call(\"get\",KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] \n" +"then\n" +" return redis.call(\"del\", KEYS[1])\n" +"else\n" +" return 0\n" +"end";String addLockLife_lua = "if redis.call(\"exists\", KEYS[1]) == 1\n" +"then\n" +" return redis.call(\"expire\", KEYS[1], ARGV[1])\n" +"else\n" +" return 0\n" +"end";public void lock() {// 判断是否可重入if (isHeldByCurrentThread()) {return;}while (!tryLock()) {try {Thread.sleep(50); // 自旋} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println("线程:" + threadName + ",占锁成功!★★★");}// 是否是当前线程占有锁,同时将超时时间重新设置,这个很重要,同样也是原子操作private boolean isHeldByCurrentThread() {List<byte[]> keys = Arrays.asList(encode(lock_key));List<byte[]> args = Arrays.asList(encode(APP_ID + String.valueOf(threadId)), encode(String.valueOf(1)));long eval = (Long) jedis.eval(encode(addLockLife_lua), keys, args);return eval == 1;}private boolean tryLock(String uuid) {SetParams setParams = new SetParams();setParams.ex(1); // 超时时间1ssetParams.nx(); // nxString response = jedis.set(lock_key, APP_ID + String.valueOf(threadId), setParams); // 转换为redis命令就是:set haolin-key xxx ex 1 nxreturn "OK".equals(response);}public void unlock(String uuid) {List<byte[]> keys = Arrays.asList(encode(lock_key));List<byte[]> args = Arrays.asList(encode(APP_ID + String.valueOf(threadId)));// 使用lua脚本,保证原子性long eval = (Long) jedis.eval(encode(releaseLock_lua), keys, args);if (eval == 1) {System.out.println("线程:" + threadName + " 释放锁成功!☆☆☆");} else {System.out.println("线程:" + threadName + " 释放锁失败!该线程未持有锁!!!");}}private byte[] encode(String param) {return param.getBytes();}
ADD_LOCK_LIFE("if redis.call(\"get\", KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1]\n" + // 判断是否是锁持有者"then\n" +" local thisLockMaxTimeKeepKey=KEYS[1] .. \":maxTime\"\n" + // 记录锁最大时间的key是:锁名字:maxTime" local nowTime=tonumber(ARGV[2])\n" + // 当前传参进来的time" local maxTime=redis.call(\"incr\", thisLockMaxTimeKeepKey)\n" + // 取出当前锁设置的最大的超时时间,如果这个保持时间的key不存在返回的是字符串nil,这里为了lua脚本的易读性,用incr操作,这样读出来的都是number类型的操作" local bigerTime=maxTime\n" + // 临时变量bigerTime=maxTime" if nowTime>maxTime-1\n" + // 如果传参进来的时间>记录的最大时间" then\n" +" bigerTime=nowTime\n" + // 则更新bigerTime" redis.call(\"set\", thisLockMaxTimeKeepKey, tostring(bigerTime))\n" + // 设置超时时间为最大的time,是最安全的" else \n" +" redis.call(\"decr\", thisLockMaxTimeKeepKey)\n" + // 当前传参time<maxTime,将刚才那次incr减回来" end\n" +" return redis.call(\"expire\", KEYS[1], tostring(bigerTime))\n" + // 重新设置超时时间为当前锁过的最大的time"else\n" +" return 0\n" +"end"),
目前为止,算上上一步中设置最大超时时间的key,加上这一步重入次数的key,加上锁本身的key,已经有3个key,需要注意的事情是,这三个key的超时时间是都要设置的!为什么? 假如说重入次数的 key没有设置超时时间,服务A节点中在一个JVM中重入了5次后,调用一次 RPC服务,RPC服务中同样重入锁,此时,锁重入次数是 6,这个时候A服务宕机,就意味着无论怎样,这把锁不可能释放了,这个分布式锁提供的完整能力,全线不可用了!
public class RedisLockIdleThreadPool {private String threadAddLife_lua = "if redis.call(\"exists\", KEYS[1]) == 1\n" +"then\n" +" return redis.call(\"expire\", KEYS[1], ARGV[1])\n" +"else\n" +" return 0\n" +"end";private volatile ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool;public RedisLockIdleThreadPool() {if (scheduledThreadPool == ) {synchronized (this) {if (scheduledThreadPool == ) {scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(); // 我这样创建线程池是为了代码的易读性,大家务必使用ThreadPoolExecutor去创建scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {addLife();}, 0, 300, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}}}}private void addLife() {// ... 省略jedis的初始化过程List<byte[]> keys = Arrays.asList(RedisLock.lock_key.getBytes());List<byte[]> args = Arrays.asList(String.valueOf(1).getBytes());jedis.eval(threadAddLife_lua.getBytes(), keys, args);}}
THREAD_ADD_LIFE("local v=redis.call(\"get\", KEYS[1]) \n" + // get key"if v==false \n" + // 如果不存在key,读出结果v是false"then \n" + // 不存在不处理"else \n" +" local match = string.find(v, ARGV[1]) \n" + // 存在,判断是否能和APP_ID匹配,匹配不上时match是nil" if match==\"nil\" \n" +" then \n" +" else \n" +" return redis.call(\"expire\", KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) \n" + // 匹配上了返回的是索引位置,如果匹配上了意味着就是当前进程占有的锁,就延长时间" end \n" +"end")
3-13、别急,还有。锁在我手里,我挂了,这...

Redis uses by default asynchronous replication, which being low latency and high performance, is the natural replication mode for the vast majority of Redis use cases.