Node.js的概念与使用
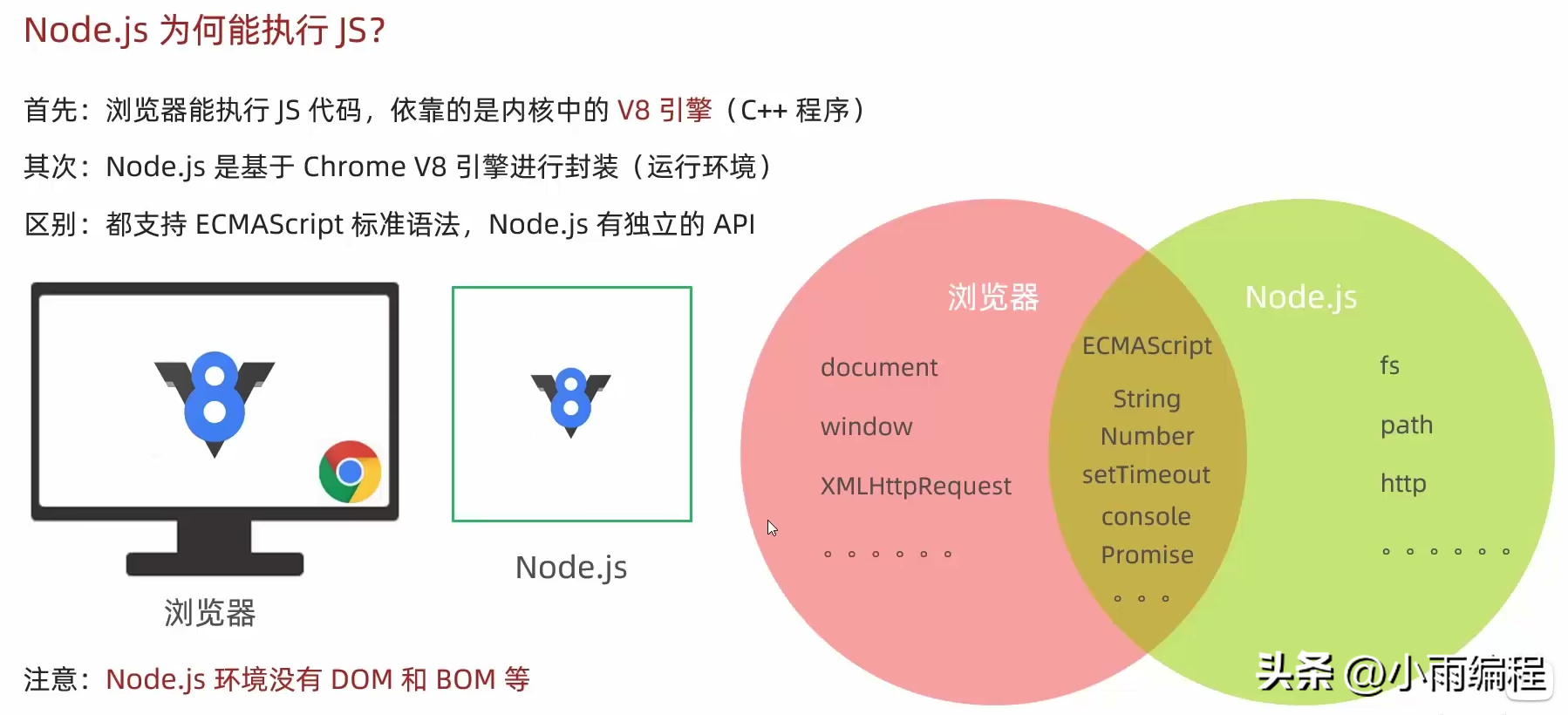
Node.js是一个跨平台的JavaScript运行环境,使得开发者可以搭建服务器端的JavaScript应用程序;
通过nvm管理nodejs版本
- Mac安装nvm
brew install nvm- 配置nvm环境变量,在~/.zshrc下添加以下内容
export NVM_DIR=~/.nvmsource $(brew --prefix nvm)/nvm.sh如果是Linux系统可以使用命令:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.38.0/install.sh | zsh执行命令source ~/.zshrc使得环境变量生效
- 安装node.js指定版本(16.19.0兼容vue-admin-template)
nvm install 16.19.0如果要安装稳定版本则使用命令:nvm install stable
二、nodejs模块
1. fs模块-读写文件
封装了与本机文件系统进行交互的方法与属性;
语法:
const fs = require('fs') // fs是读写模块的标识符fs.writeFile('文件路径','写入内容',err => { // 写入后的回调函数 })fs.readFile('文件路径',(err,data) => { // 读取后的回调函数 // data是文件内容的Buffer数据流,可以通过toString方法转为字符串})案例:
使用fs模块写入字符串到文件以及从文件中读取内容
// 导入fs模块const fs = require('fs');// 文件写入fs.writeFile('./1.txt','hello, this is javascript',error => { if(error){ console.log(err); }else{ console.log('写入成功'); }})// 文件读取fs.readFile('./1.txt',(err,data)=>{ if(err){ console.log(err); }else{ console.log(data.toString()); }})2.path模块-路径处理
建议在Node.js中使用绝对路径;
js中可以使用--dirname获取当前程序运行的绝对路径;
使用path.join()可以生成作用于当前平台的分隔符将路径片段连接在一起;
语法:
const path = require('path')path.join('path1','path2',...)案例:
压缩前端html文件,去掉回车符\r和\n,写入到新的HTML文件中;
const fs = require('fs');const path = require('path');fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname,'public/index.html'),(error,data) => { if(error){ console.log(error); }else{ const str = data.toString(); // 利用正则表达式去除回车与换行 const resStr = str.replace(/[\r\n]/g,''); console.log(resStr); // 写入新的文件中 fs.writeFile(path.join(__dirname,'dist/index.html'),resStr,error => { if(error){ console.log(error); }else{ console.log('写入成功!'); } }) }})正则表达式中[ ]代表的是一个字符串类,使用g代表全局匹配;
如果使用这种正则删除回车与换行,那么HTML中如果写了JavaScript就需要删除双斜杠注释内容,否则这种方式压缩会导致注释符号将所有JavaScript代码注释掉;
3.Http模块
URL是统一资源定位符,端口号标记服务器里不同功能的服务程序,端口号范围0-65535,Http协议默认访问80端口;
案例:创建web服务并相应内容给服务器;
语法:
const http = require('http')const server = http.createServer()server.on('request',(req,res) => { // 设置响应头:内容类型,普通文本;编码格式为utf-8 res.setHeader('Content-Type','text/plain;charset=utf-8') // 设置响应体 res.end('您好,欢迎使用Nodejs创建的web服务')})server.listen(3000,() => { console.log('web服务已经启动')})案例:创建一个web服务,浏览器访问/index.html时,返回指定网页内容;
const http = require('http');const fs = require('fs');const path = require('path');const server = http.createServer()server.on('request', (req, res) => { if (req.url === '/ ') { fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, 'dist/index.html'), (err, data) => { res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html;charset=utf-8'); res.end(data.toString()); }) } else { res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html;charset=utf-8'); res.end('您访问的路径不存在'); }})server.listen(80, () => { console.log('web服务已经启动');})4.项目模块化

4.1 CommonJS标准
定义:在Nodejs中,每个文件都被视为一个单独的模块;
CommonJS标准语法 :
导出 model.exports={}
导入 require('模块名或路径')
const obj = require('模块名或路径')// obj 等于module.exports导出的对象const baseURL = 'http://hmajax.itheima.net'const getArraySum = arr => arr.reduce((sum,val) => sum += val, 0)module.exports={ 对外属性名1: baseURL, 对外属性名2: getArraySum}案例:写一个util.js工具模块,使用CommonJS的语法,定义返回baseURL和数组求和的方法,在另一个JS模块中导入并应用该方法;
// util.jsconst baseURL = 'http://hmajax.itheima.net'const getArraySum = array => array.reduce((sum,val)=>sum += val,0)module.exports = { url:baseURL, arraySum: getArraySum}// demo.jsconst obj = require('./util.js');console.log(obj);const res = obj.arraySum([1,2,3,4]);console.log(res);4.2 ECMAScript标准
4.2.1 默认导出导入用法:
const baseURL = 'http://hmajax.itheima.net'const getArraySum = arr => arr.reduce((sum,val) => sum += val, 0)export default { 对外属性名1: baseURL, 对外属性名2: getArraySum}导出export default {}
导入import 变量名 from '模块名或路径'
Node.js默认支持CommonJS标准语法,如果需要使用ECMAScript语法,在运行模块所在文件夹新建package.json文件,并写入{"type":"module"}
案例:写一个util.js工具模块,使用ECMAScript的语法,定义返回baseURL和数组求和的方法,在另一个JS模块中导入并应用该方法;
// utils.jsconst baseURL = 'http://hmajax.itheima.net'const getArraySum = arr => arr.reduce((sum,val) => sum += val, 0)export default { url: baseURL, arraySum: getArraySum}// package.json{ "type":"module"}// demo.jsimport obj from './util.js'console.log(obj);const res = obj.arraySum([1,2,3,4]);console.log(res);4.2.2 命名导出和导入用法:
导出:export 修饰定义语句
export const baseURL = 'http://hmajax.itheima.net'export const getArraySum = arr => arr.reduce((sum,val) => sum += val, 0)导入:import {同名变量} from '模块名或者路径'
import {baseURL,getArraySum} from '模块名或路径'案例:使用命名导出的方式,定义返回baseURL和数组求和的方法,在另一个JS模块中导入并应用该方法;
// utils.jsexport const baseURL = 'http://hmajax.itheima.net'export const getArraySum = arr => arr.reduce((sum,val) => sum += val, 0)// package.json{ "type":"module"}// demo.jsimport {baseURL,getArraySum} from './util.js'console.log(baseURL);console.log(getArraySum([1,2,3,4]));5. Nodejs中的包
5.1 包的概念
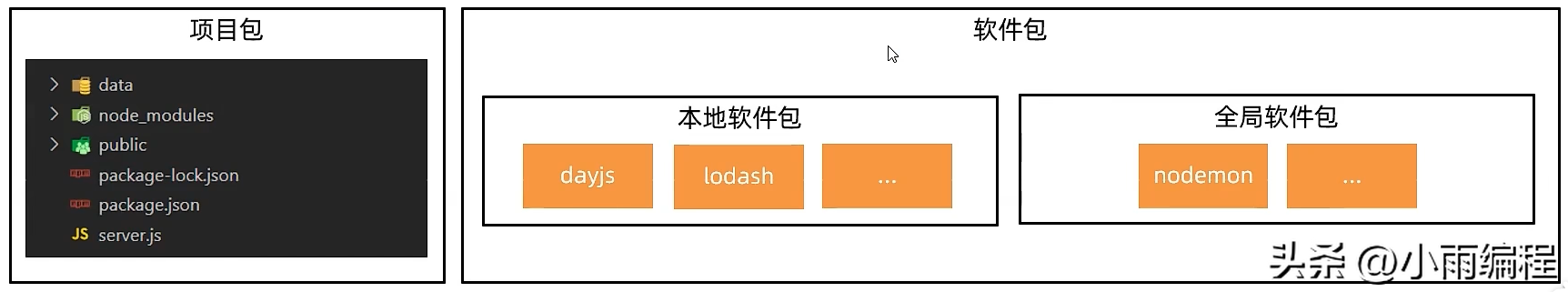
概念:将模块、代码、和其他资料聚合成一个文件夹;
分类:主要分为项目包(编写项目和业务逻辑)和软件包(封装工具和方法)
根目录有package.json文件用于记录包的清单信息(作者、入口文件、包名)
导入一个包文件夹时,默认导入的是index.js文件,如果没有这个文件,就去package.json里找main定义的文件;
一个包的项目文件结构::point_down:
├── server.js // 实际写的业务逻辑代码,在这里导入包utils└── utils // 包文件夹 ├── index.js // 这里将arr.js和str.js导出的功能函数进行聚合,导包实际导的是这个js文件 ├── lib // 功能函数文件夹 │ ├── arr.js // 实现具体功能 │ └── str.js // 实现具体功能 └── package.json // 记录包的清单信息,定义入口js文件是谁,默认是index.js案例:
// server.jsconst obj = require('./utils') const res = obj.getArraySum([1,2,3,3]);console.log(res);// index.js// 不解构会得到嵌套对象,这里直接解构赋值const {getArraySum} = require('./lib/arr.js');const {checkUser,checkPwd} = require('./lib/str.js');module.exports={ getArraySum, checkUser, checkPwd}// arr.jsconst getArraySum = arr => arr.reduce((sum,val) => sum += val,0)module.exports = { getArraySum}// str.jsconst checkUserName = username => { return username.length >= 8;}const checkPassWord = password => { return password.length >= 6;}module.exports = { checkUser:checkUserName, checkPwd:checkPassWord,}5.2 npm包管理器
安装本地软件包
初始化清单文件npm init -y,会在当前文件夹下生成一个package.json文件
下载软件包:npm i 软件包名,下载包的同时会继续生成package-lock.json文件用于固化软件包的版本,防止最新版本更新影响本地;
安装所有依赖:npm -i会将package.json中声明的包名以及对应版本号都下载到,node-modules文件夹里;
删除软件包:npm uni 软件包名;
安装全局软件包
本地软件包在当前项目中使用,存在于node_modules中;
全局软件包对于本机所有项目都可用,存在于系统设置的位置;
这里以安装nodemon为例:
nodemon可以实时检测代码的更改,自动启动程序;
使用:
安装npm i nodemon -g;
运行 nodemon 待启动的js文件
至此,你就学会了nodejs的基本使用啦~
 鲁公网安备37020202000738号
鲁公网安备37020202000738号