更多深度文章,欢迎访问云计算频道:
https://yq.aliyun.com/cloud
标签
PostgreSQL , vector grid , polygon grid , square grid , Hexagon grid , 矢量网格 , 几何网格 , 线段网格 , 多边形网格 , 四边形网格 , 六边形网格 , 蜂巢 , PostGIS , 地图 , 转换
背景
人们为了更好的描述一个东西,有一种将大化小的思路,比如时钟被分为了12个区域,每个区域表示一个小时,然后每个小的区域又被划分为更小的区域表示分钟。
在GIS系统中,也有类似的思想,比如将地图划分成网格。通过编码来简化地理位置的判断(比如相交,包含,距离计算等),但是请注意使用网格带来的问题,比如精度的问题,网格的大小决定了精度,又比如相对坐标的问题,可能无法描述清楚边界的归属。
PS:
1. 在PostGIS中虽然也支持网格对象的描述方式,但是并不是使用这种方法来进行几何运算(比如相交,包含,距离计算等),所以不存在类似的精度问题,个人建议没有强需求的话,不必做这样的网格转换。
PostgreSQL GIS索引的原理请参考
《从难缠的模糊查询聊开 - PostgreSQL独门绝招之一 GIN , GiST , SP-GiST , RUM 索引原理与技术背景》
2. 如果是多种精度地图的切换(比如多个图层,每个图层代表一种地图精度),建议使用辐射的方式逐渐展开更精细的图层,以点为中心,逐渐辐射。(很多专业的地图软件是这样做的)
回到主题,还记得最强大脑的蜂巢迷宫吗?
还有勤劳的蜜蜂兄弟
我们接下来要做的就是如何将几何图形转换为网格对象。
回忆一下六边形的几何特性
首先要了解一下六边形的几何特性,提供转换的计算基础。
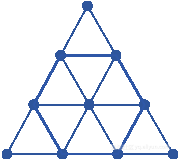
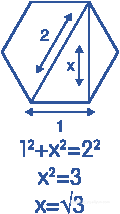
六边形可以切分为6个等边三角形
所以它的边长关系如下
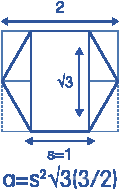
面积计算
更多细节详见
https://hexnet.org/content/hexagonal-geometry
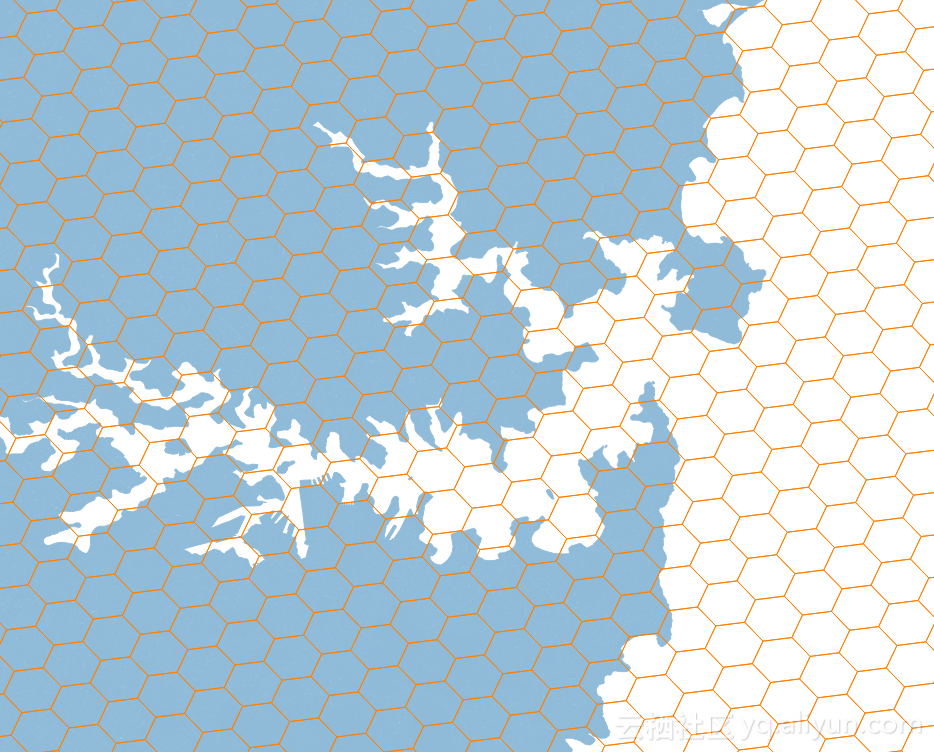
将几何图形(sharp)转换为六边形网格
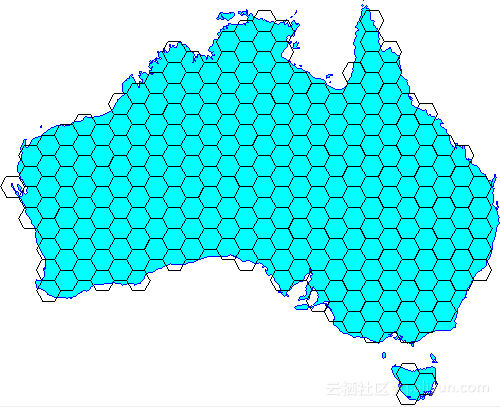
比如要将澳大利亚的版图,转换为六边形网格,
有两种方法,一种使用geotools的JAVA 类(在程序中转换),另一种是使用PostGIS插件的UDF(在数据库中转换)。
当然,如果PostgreSQL安装了pljava插件的话,那么也可以在PostgreSQL中调用geotools提供的java类进行转换。
下面是例子
1 geotools Vector grids class
http://docs.geotools.org/latest/userguide/extension/grid.html
使用geotools vector grids class生成网格,返回 SimpleFeatureSource 类型。
geotools Vector grids class支持将几何图形转换为 polygon网格 或者 line网格 。
1 Polygon grids
举几个例子
1. 将澳大利亚地图转换为10度边长的正方形网格
输入澳大利亚的经纬度范围,转换
ReferencedEnvelope gridBounds = new ReferencedEnvelope( 110.0, 150.0, -45.0, -5.0, DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84); SimpleFeatureSource grid = Grids.createSquareGrid(gridBounds, 10.0);
2. 将澳大利亚地图转换为最大20度边长的扇形网格
ReferencedEnvelope gridBounds = new ReferencedEnvelope( 110, 160, -45, -8, DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84); double squareWidth = 20.0; // max distance between vertices double vertexSpacing = squareWidth / 20; SimpleFeatureSource grid = Grids.createSquareGrid(gridBounds, squareWidth, vertexSpacing);
3. 创建纵横宽100,变长为5.0的六边形网格
ReferencedEnvelope gridBounds = new ReferencedEnvelope(0, 100, 0, 100, null); // length of each hexagon edge double sideLen = 5.0; SimpleFeatureSource grid = Grids.createHexagonalGrid(gridBounds, sideLen);
4. 导入图形、将澳大利亚地图转换为边长1度的六边形网格
自定义图形边界判断的类
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Coordinate; import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Geometry; import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.GeometryFactory; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Map; import org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureSource; import org.geotools.factory.CommonFactoryFinder; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.JTSFactoryFinder; import org.opengis.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureType; import org.opengis.filter.Filter; import org.opengis.filter.FilterFactory2; public class IntersectionBuilder extends GridFeatureBuilder { final FilterFactory2 ff2 = CommonFactoryFinder.getFilterFactory2(); final GeometryFactory gf = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory(); final SimpleFeatureSource source; int id = 0; public IntersectionBuilder(SimpleFeatureType type, SimpleFeatureSource source) { super(type); this.source = source; } public void setAttributes(GridElement el, Map<String, Object> attributes) { attributes.put("id", ++id); } @Override public boolean getCreateFeature(GridElement el) { Coordinate c = ((PolygonElement) el).getCenter(); Geometry p = gf.createPoint(c); Filter filter = ff2.intersects(ff2.property("the_geom"), ff2.literal(p)); boolean result = false; try { result = !source.getFeatures(filter).isEmpty(); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } return result; } }导入地图,在createHexagonalGrid中使用边界判断的类,生成六边形网格
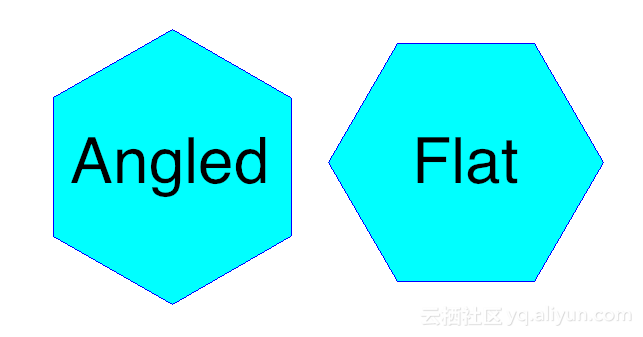
// Load the outline of Australia from a shapefile URL url = getClass().getResource("oz.shp"); FileDataStore dataStore = FileDataStoreFinder.getDataStore(url); SimpleFeatureSource ozMapSource = dataStore.getFeatureSource(); // Set the grid size (1 degree) and create a bounding envelope // that is neatly aligned with the grid size double sideLen = 1.0; ReferencedEnvelope gridBounds = Envelopes.expandToInclude(ozMapSource.getBounds(), sideLen); // Create a feature type SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder tb = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder(); tb.setName("grid"); tb.add(GridFeatureBuilder.DEFAULT_GEOMETRY_ATTRIBUTE_NAME, Polygon.class, gridBounds.getCoordinateReferenceSystem()); tb.add("id", Integer.class); SimpleFeatureType TYPE = tb.buildFeatureType(); // Build the grid the custom feature builder class GridFeatureBuilder builder = new IntersectionBuilder(TYPE, ozMapSource); SimpleFeatureSource grid = Grids.createHexagonalGrid(gridBounds, sideLen, -1, builder);5. 生成的六边形网格的摆放参数,横(flat)的还是竖(angled)的?
默认为flat网格,如果要生成angled网格,如下
ReferencedEnvelope gridBounds = new ReferencedEnvelope(0, 100, 0, 100, null); double sideLen = 5.0; GridFeatureBuilder builder = new DefaultGridFeatureBuilder(); SimpleFeatureSource grid = Hexagons.createGrid( gridBounds, sideLen, HexagonOrientation.ANGLED, builder);
2 line grids
转换为line 网格
例子
ReferencedEnvelope gridBounds = new ReferencedEnvelope( 110.0, 150.0, -45.0, -5.0, DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84); /* * Line definitions: * major lines at 10 degree spacing are indicated by level = 2 * minor lines at 2 degree spacing are indicated by level = 1 * (level values are arbitrary; only rank order matters) */ List<OrthoLineDef> lineDefs = Arrays.asList( // vertical (longitude) lines new OrthoLineDef(LineOrientation.VERTICAL, 2, 10.0), new OrthoLineDef(LineOrientation.VERTICAL, 1, 2.0), // horizontal (latitude) lines new OrthoLineDef(LineOrientation.HORIZONTAL, 2, 10.0), new OrthoLineDef(LineOrientation.HORIZONTAL, 1, 2.0)); // Specify vertex spacing to get "densified" polygons double vertexSpacing = 0.1; SimpleFeatureSource grid = Lines.createOrthoLines(gridBounds, lineDefs, vertexSpacing);
2 PostGIS UDF hex-grid
https://github.com/minus34/postgis-scripts/tree/master/hex-grid
PostGIS不需要多介绍了,几十年的老牌GIS插件,在军方、科研、民用等各个领域有着非常广泛对应用。
如果你使用了PostGIS插件的话,在里面存储了不管是geometry, polygon还是其他的地图类型,都可以转换为六边形网格。
转换时使用这些定义好的UDF即可。
UDF使用方法
See the 2 sample usage scripts to see how to create a national hex grid, using the function.
UDF输入参数
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| areakm2 | Area of each hexagon in square km. Note: output hexagon sizes can be off slightly due to coordinate rounding in the calcs. |
| xmin,ymin | Minimum coordinates of the grid extents (i.e. bottom, left). |
| xmax,ymax | Maximum coordinates of the grid extents (i.e. top, right). |
| inputsrid | The coordinate system (SRID) of the min/max coordinates. |
| workingsrid | The SRID used to process the hexagons: |
| - | SRID must be a projected coord sys (i.e. in metres) as the calcs require ints. Degrees are out. |
| - | Should be an equal area SRID - i.e. Albers or Lambert Azimuthal (e.g. Australia = 3577, US = 2163). |
| - | Using a Mercator projection will NOT return hexagons of equal area (don't try it in Greenland). |
| ouputsrid | The SRID of the output hexagons. |
输出
A set of hexagonal polygons as PostGIS geometries
转换基础,参考如下
https://trac.osgeo.org/postgis/wiki/UsersWikiGenerateHexagonalGrid
小结
1. 在PostGIS中虽然也支持网格对象的描述方式,但是并不是使用网格编码的方法来进行几何运算(比如相交,包含,距离计算等),而是类似矢量的计算方法,因此不存在网格的精度问题,个人建议没有强需求的话,不必将几何图形转换为网格。
PostgreSQL GIS索引的原理请参考
《从难缠的模糊查询聊开 - PostgreSQL独门绝招之一 GIN , GiST , SP-GiST , RUM 索引原理与技术背景》
2. 如果是多种精度地图的切换(比如多个图层,每个图层代表一种地图精度),建议使用辐射的方式逐渐展开更精细的图层,以点为中心,逐渐辐射。(很多专业的地图软件是这样做的)
3. 如果要将图形转换为网格,可以使用geotools提供的java class来转换,也可以使用PostGIS的UDF来转换,当然PostgreSQL如果安装了pljava过程语言的话,可以直接在数据库中调用geotools提供的java class对图形进行转换。
4. pljava
https://tada.github.io/pljava/
参考
1. geotools vector grid包
http://docs.geotools.org/latest/userguide/extension/grid.html
2. PostGIS 生成六边形网格的UDF
https://github.com/minus34/postgis-scripts/tree/master/hex-grid
3. PostGIS 生成六边形网格的算法基础
https://trac.osgeo.org/postgis/wiki/UsersWikiGenerateHexagonalGrid
4. 六边形几何公式
https://hexnet.org/content/hexagonal-geometry




 鲁公网安备37020202000738号
鲁公网安备37020202000738号