介绍
字符串是Java中的一个特殊类。我们在Java程序中经常使用字符串,所以比较两个字符串是Java中的一种常见做法。在本文中,我尝试回答关于字符串的最常见问题,比如:“如何在Java中比较字符串?”
在验证、排序、引用匹配等过程中,比较字符串非常有用。
我列出了在Java中比较字符串的三种不同方法。
使用equals()方法(比较内容)
使用==操作符(比较对象引用)
使用compareTo()方法(按字母顺序比较字符串)

1.使用Equals() 方法比较字符串
这样,我正在使用 .equals() String类的实例方法。.equals() 方法原本 是 Object 类方法,而String类会覆盖它。
equals() 方法比较两个字符串的值相等性,无论它们在逻辑上是否相等。
equals() String类中的方法将另一个字符串作为参数,并将其与指定的字符串进行比较。true 当且仅当参数字符串不为null且包含与指定字符串相同的字符时,它返回 。
public boolean equals(Object anObject)It compare this string with the argument strings and return true if the argument is not null and contains the same character as the specified string.param -another stringreturns -true - if argument is not null and it contains same characters as the specified string13ex. firstString.equals(secondString)14// returns true if and only if the secondString is not null and contains the same characters as firstString.已要求程序使用以下equals() 方法比较字符串 :
/**2 * A Java program to compare two strings using equsls()3 * and equalsIgnoreCase() method of the String.4 * 5 * @author Gaurav Kukade at coderolls.com6 */78public class CompareUsingEquals {910 public static void main(String[] args) {11 String firstString = "coderolls";12 String secondString = "javablog";13 String thirdString = "coderolls";14 String fourthString = "CodeRolls";1516 System.out.println("Comparing strings using equals() and equalsIgnoreCase() method\n");1718 // Using equals() method19 System.out.println(firstString.equals(secondString)); System.out.print("firstString.equals(thirdString) : "); System.out.println(firstString.equals(thirdString)); /* * Using equalsIgnoreCase() method to ignore * case consideration (i.e. Capital or small) of both the strings. */ System.out.print("firstString.equalsIgnoreCase(fourthString) : "); System.out.println(firstString.equalsIgnoreCase(fourthString)); }}输出:
Comparing strings using equals() and equalsIgnoreCase() methodfirstString.equals(secondString) : falsefirstString.equals(thirdString) : truefirstString.equalsIgnoreCase(fourthString) : true2. 使用==操作符比较字符串
在String中,==操作符用于比较给定字符串的引用,这取决于它们是否引用相同的对象。
当使用==操作符比较两个字符串时,如果字符串变量指向相同的java对象,则返回true。否则,它将返回false。
我已经给出了一个Java程序来比较使用==操作符如下:
/ ** *一个Java程序,用于使用==运算符比较字符串。 * * ==运算符会终止是否两个字符串都引用 *到相同的String对象。 * /public class CompareUsingEqualsToOperator { public static void main(String[] args) { String firstString = "coderolls"; String secondString = "javablog"; String thirdString = "coderolls"; //建具有与firstString或thirdString相同值的新String对象 String fourthString = new String("coderolls"); System.out.println("Comparing strings using == operator \n"); System.out.print("firstString == secondString : "); System.out.println(firstString == secondString); / * *这里firstString和thirdString指的是相同的String对象 * / System.out.print("firstString == thirdString : "); System.out.println(firstString == thirdString); /* * Here firstString and fourthString have same value * but they are referring to the different String object. * * hence it will print 'false' */ System.out.print("firstString == fourthString : "); System.out.println(firstString == fourthString); }}输出:
Comparing strings using == operator firstString == secondString : falsefirstString == thirdString : truefirstString == fourthString : false使用==操作符进行字符串比较的问题
大多数初学Java的开发人员都会犯这个错误,他们使用==操作符比较两个字符串。
逻辑上,它们必须检查两个字符串是否包含相同的字符序列。
在Java字符串中,==操作符用于检查字符串对象和equals()方法的引用,equals()方法用于检查两个字符串的值是否相等。
== -检查引用是否相等
equals()——检查值是否相等
当我们将字符串值赋给字符串变量时,JVM将检查字符串池中是否已经存在具有相等值的字符串。如果它不在字符串池中,它将被添加到常量池中,并返回对该字符串对象的引用。
如果它存在于字符串池中,则返回对该字符串对象的内存地址的引用。
下面的图像显示了同样的图形解释。
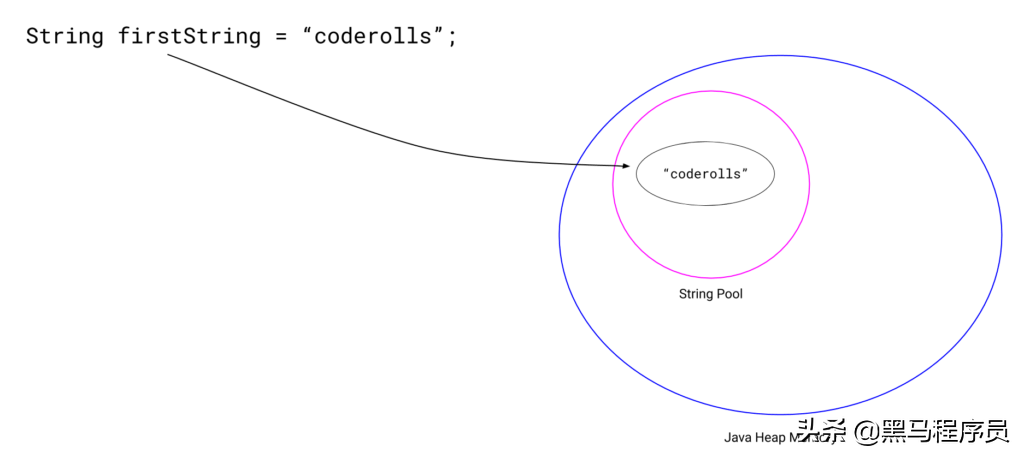
在上方,我们firstString指向字符串池中的“ coderolls”字符串。
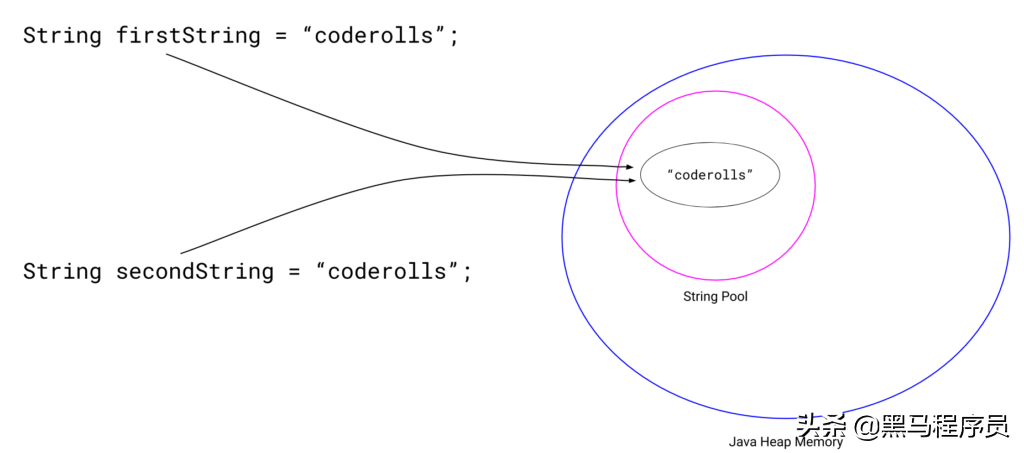
如果我们将相等的值分配给另一个字符串变量,JVM将检查具有该值的字符串是否出现在字符串常量池中。
由于在前面的步骤中已经创建了具有该值的string对象,所以另一个string变量开始引用前面创建的string对象实例。
下面的图像显示了“firstString”和“secondString”的图形说明,它们指向字符串池中的“coderolls”字符串。
当我们使用new 运算符创建字符串时,将创建一个 新的字符串对象并将其存储在Java堆空间中。
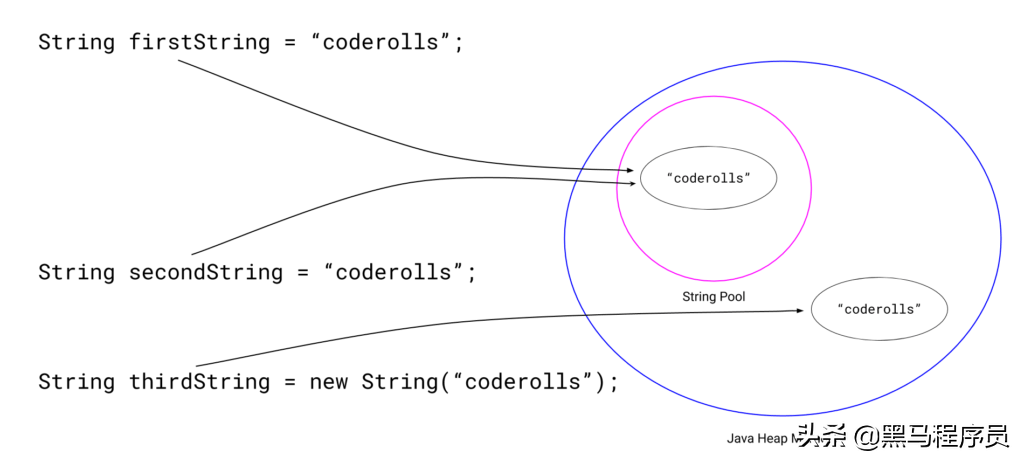
在上方,我们可以看到' firstString'和' secondString'指向coderolls字符串池中的“ ”字符串,而' thirdString'指向coderollsJava堆空间中的“ ”。
如果参数字符串在词法上大于指定字符串,也就是说,如果参数字符串在指定字符串之后,那么它返回一个负整数。(参数字符串>指定字符串)
如果参数字符串在字典上比指定字符串小,也就是说,如果参数字符串在指定字符串之前,则返回正整数。(参数字符串<指定字符串)
如果两个字符串都是lexicographic equals,则返回0。(参数字符串=指定字符串)
如果想忽略两个字符串的情况,请使用compareToIgnoreCase()方法。
我已经给出了一个使用compareTo()方法比较字符串的程序。它还包含一个用compareToIgnoreCase()方法忽略案例的案例。
/**2 * A Java program to compare strings using compareTo()3 * and compareToIgnoreCase() method.4 * 5 * compareTo() compare strings lexicograpgically.6 * 7 * @author Gaurav Kukade at coderolls.com8 */910public class CompareUsingCompareTo {1112 public static void main(String[] args) {13 14 String firstString = "java";15 String secondString = "coderolls";16 String thirdString = "sql";17 String fourthString = "CodeRolls";18 19 System.out.println("Comparing strings using compareTo() and compareToIgnoreCase() method\n");20 21 // Using compareTo() method22 System.out.println(firstString.compareTo(secondString)); System.out.print("firstString.compareTo(thirdString) : "); System.out.println(firstString.compareTo(thirdString)); /*29 * Using compareToIgnoreCase() method to ignore30 * case consideration (i.e. Capital or small) of both the strings.31 */ System.out.print("secondString.compareToIgnoreCase(fourthString) : "); System.out.println(secondString.compareToIgnoreCase(fourthString)); }}输出:
Comparing strings using compareTo() and compareToIgnoreCase() methodfirstString.compareTo(secondString) : 7firstString.compareTo(thirdString) : -9secondString.compareToIgnoreCase(fourthString) : 0结论
我们可以用下面的方法来比较字符串:
在字符串中使用equals()方法:equals()方法用于检查字符串值是否包含相同的字符序列。
使用==操作符:==操作符检查两个字符串的引用是否相等,是否指向同一个字符串对象。
使用compareTo()方法:compareTo()方法用于按字母顺序检查字符串。查看关于如何按字典顺序比较字符串的详细文章。
大多数初学Java的开发人员在比较字符串时都会出错。他们想要检查字符串的内容,但是他们使用==操作符来检查它。
总是建议使用equals()方法根据字符串的内容比较字符串。
 鲁公网安备37020202000738号
鲁公网安备37020202000738号