最爱折腾的就是前端工程师了,从 jQuery 折腾到 AngularJs,再折腾到 Vue、React。最爱跨屏的也是前端工程师,从 phonegap,折腾到 React Native,这不又折腾到了 Flutter。
作者:hicc;来源:腾讯技术工程

低成本地为用户带来更优秀的用户体验。
目前来说Flutter可能是其中最优秀的一种方案了。
Flutter 是什么?
Flutter is Google’s UI toolkit for building beautiful, natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase.
Flutter是由原 Google Chrome 团队成员,利用 Chrome 2D 渲染引擎,然后精简 CSS 布局演变而来。
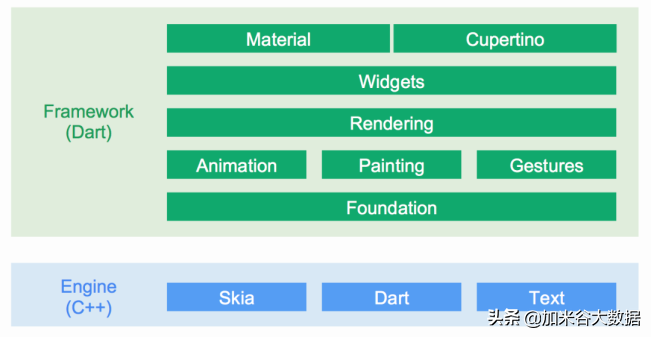
或者更详细的版本
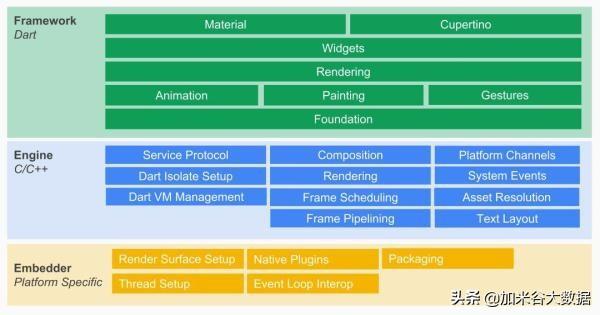
- Flutter 在各个原生的平台中,使用自己的 C++的引擎渲染界面,没有使用 webview,也不像 RN、NativeScript 一样使用系统的组件。简单来说平台只是给 Flutter 提供一个画布。
- 界面使用 Dart 语言开发,貌似唯一支持 JIT,和 AOT 模式的强类型语言。
- 写法非常的现代,声明式,组件化,Composition > inheritance,响应式……就是现在前端流行的这一套
- 一套代码搞定所有平台。
Flutter 为什么快?Flutter 相比 RN 的优势在哪里?
从架构中实际上已经能看出 Flutter 为什么快,至少相比之前的当红炸子鸡 React Native 快的原因了。
- Skia 引擎,Chrome, Chrome OS,Android,Firefox,Firefox OS 都以此作为渲染引擎。
- Dart 语言可以 AOT 编译成 ARM Code,让布局以及业务代码运行的最快,而且 Dart 的 GC 针对 Flutter 频繁销毁创建 Widget 做了专门的优化。
- CSS 的的子集 Flex like 的布局方式,保留强大表现能力的同时,也保留了性能。
- Flutter 业务书写的 Widget 在渲染之前 diff 转化成 Render Object,对,就像 React 中的 Virtual DOM,以此来确保开发体验和性能。
而相比 React Native:
- RN 使用 JavaScript 来运行业务代码,然后 JS Bridge 的方式调用平台相关组件,性能比有损失,甚至平台不同 js 引擎都不一样。
- RN 使用平台组件,行为一致性会有打折,或者说,开发者需要处理更多平台相关的问题。
而具体两者的性能测试,可以看这里,结论是 Flutter,在 CPU,FPS,内存稳定上均优于 ReactNative。
Dart 语言
在开始 Flutter 之前,我们需要先了解下 Dart 语言……
Dart 是由 Google 开发,最初是想作为 JavaScript 替代语言,但是失败沉寂之后,作为 Flutter 独有开发语言又焕发了第二春 。
实际上即使到了 2.0,Dart 语法和 JavaScriptFlutter非常的相像。单线程,Event Loop……
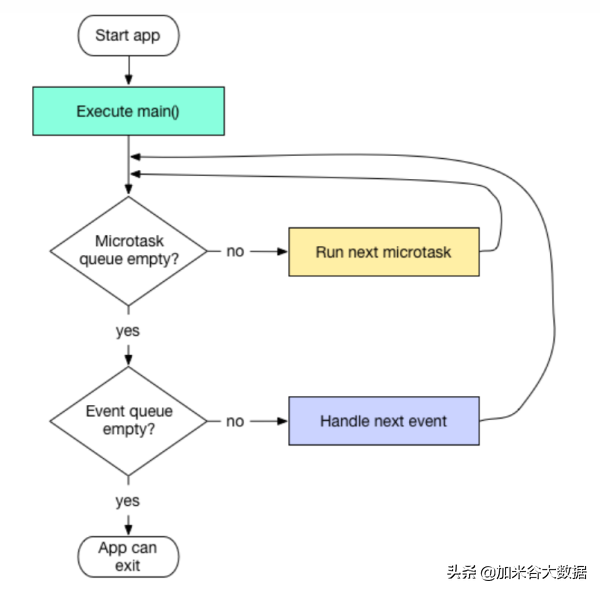
当然作为一篇写给前端工程师的教程,我在这里只想写写 JavaScript 中暂时没有的,Dart 中更为省心,也更“甜”的东西。
- 不会飘的this
- 强类型,当然前端现在有了 TypeScript
- 强大方便的操作符号:
- ?. 方便安全的foo?.bar取值,如果 foo 为null,那么取值为null
- ?? condition ? expr1 : expr2 可以简写为expr1 ?? expr2
- =和其他符号的组合: *=、~/=、&=、|= ……
- 级联操作符(Cascade notation ..)
// 想想这样省了多少变量声明 querySelect('#button') ..text ="Confirm" ..classes.add('important') ..onClick.listen((e) => window.alert('Confirmed')) 甚至可以重写操作符
class Vector { final int x, y; Vector(this.x, this.y); Vector operator +(Vector v) => Vector(x + v.x, y + v.y); Vector operator -(Vector v) => Vector(x - v.x, y - v.y); // Operator == and hashCode not shown. For details, see note below. // ··· } void main() { final v = Vector(2, 3); final w = Vector(2, 2); assert(v + w == Vector(4, 5)); assert(v - w == Vector(0, 1)); } 注:重写==,也需要重写 Object hashCodegetter
class Person { final String firstName, lastName; Person(this.firstName, this.lastName); // Override hashCode using strategy from Effective Java, // Chapter 11. @override int get hashCode { int result = 17; result = 37 * result + firstName.hashCode; result = 37 * result + lastName.hashCode; return result; } // You should generally implement operator == if you // override hashCode. @override bool operator ==(dynamic other) { if (other is! Person) return false; Person person = other; return (person.firstName == firstName && person.lastName == lastName); } } void main() { var p1 = Person('Bob', 'Smith'); var p2 = Person('Bob', 'Smith'); var p3 = 'not a person'; assert(p1.hashCode == p2.hashCode); assert(p1 == p2); assert(p1 != p3); } 这点在 diff 对象的时候尤其有用。
lsolate
Dart 运行在独立隔离的 iSolate 中就类似 JavaScript 一样,单线程事件驱动,但是 Dart 也开放了创建其他 isolate,充分利用 CPU 的多和能力。
loadData() async { // 通过spawn新建一个isolate,并绑定静态方法 ReceivePort receivePort =ReceivePort(); await Isolate.spawn(dataLoader, receivePort.sendPort); // 获取新isolate的监听port SendPort sendPort = await receivePort.first; // 调用sendReceive自定义方法 List dataList = await sendReceive(sendPort, 'https://hicc.me/posts'); print('dataList $dataList'); } // isolate的绑定方法 static dataLoader(SendPort sendPort) async{ // 创建监听port,并将sendPort传给外界用来调用 ReceivePort receivePort =ReceivePort(); sendPort.send(receivePort.sendPort); // 监听外界调用 await for (var msg in receivePort) { String requestURL =msg[0]; SendPort callbackPort =msg[1]; Client client = Client(); Response response = await client.get(requestURL); List dataList = json.decode(response.body); // 回调返回值给调用者 callbackPort.send(dataList); } } // 创建自己的监听port,并且向新isolate发送消息 Future sendReceive(SendPort sendPort, String url) { ReceivePort receivePort =ReceivePort(); sendPort.send([url, receivePort.sendPort]); // 接收到返回值,返回给调用者 return receivePort.first; } 当然 Flutter 中封装了compute,可以方便的使用,譬如在其它 isolate 中解析大的 json。
Dart UI as Code
在这里单独提出来的意义在于,从 React 开始,到 Flutter,到最近的 Apple SwiftUI,Android Jetpack Compose 声明式组件写法越发流行,Web 前端使用 JSX 来让开发者更方便的书写,而 Flutter,SwiftUI 则直接从优化语言本身着手。
函数类的命名参数
void test({@required int age,String name}) { print(name); print(age); } // 解决函数调用时候,参数不明确的问题 test(name:"hicc",age: 30) // 这样对于组件的使用尤为方便 class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar(), body: Container(), floatingActionButton:FloatingActionButton() ); } } 大杀器:Collection If 和 Collection For
// collection If Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Row( children: [ IconButton(icon: Icon(Icons.menu)), Expanded(child: title), if (!isAndroid) IconButton(icon: Icon(Icons.search)), ], ); } // Collect For var command = [ engineDartPath, frontendServer, for (var root in fileSystemRoots) "--filesystem-root=$root", for (var entryPoint in entryPoints) if (fileExists("lib/$entryPoint.json")) "lib/$entryPoint", mainPath ]; 更多 Dart 2.3 对此的优化看这里。
Flutter 怎么写
到这里终于到正题了,如果熟悉 web 前端,熟悉 React 的话,你会对下面要讲的异常的熟悉。

Flutter App 的一切从lib/main.dart文件的 main 函数开始:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() => runApp(MyApp()); class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'Welcome to Flutter', home: Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text('Welcome to Flutter'), ), body: Center( child: Text('Hello World'), ), ), ); } } Dart 类 build 方法返回的便是 Widget,在 Flutter 中一切都是 Widget,包括但不限于
- 结构性元素,menu,button 等
- 样式类元素,font,color 等
- 布局类元素,padding,margin 等
- 导航
- 手势
Widget 是 Dart 中特殊的类,通过实例化(Dart 中new 是可选的)相互嵌套,你的这个 App 就是形如下图的一颗组件树(Dart 入口函数的概念,main.dart -> main())。
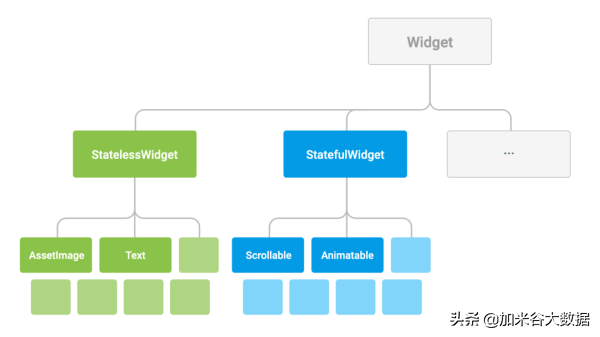
Widget 布局
上说过 Flutter 布局思路来自 CSS,而 Flutter 中一切皆 Widget,因此整体布局也很简单:
- 容器组件 Container
- decoration 装饰属性,设置背景色,背景图,边框,圆角,阴影和渐变等
- margin
- padding
- alignment
- width
- height
- Padding,Center
- Row,Column,Flex
- Wrap, Flow 流式布局
- Stack, Z 轴布局
- ……
Flutter 中 Widget 可以分为三类,形如 React 中“展示组件”、“容器组件”,“context”。
StatelessWidget
这个就是 Flutter 中的“展示组件”,自身不保存状态,外部参数变化就销毁重新创建。Flutter 建议尽量使用无状态的组件。
StatefulWidget
状态组件就是类似于 React 中的“容器组件”了,Flutter 中状态组件写法会稍微不一样。
class Counter extends StatefulWidget { // This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the // values (in this case nothing) provided by the parent and used by the build // method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are always marked "final". @override _CounterState createState() => _CounterState(); } class _CounterState extends State<Counter> { int _counter = 0; void _increment() { setState(() { // This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that // something has changed in this State, which causes it to rerun // the build method below so that the display can reflect the // updated values. If you change _counter without calling // setState(), then the build method won't be called again, // and so nothing would appear to happen. _counter++; }); } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { // This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance // as done by the _increment method above. // The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning // build methods fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that // needs updating rather than having to individually change // instances of widgets. return Row( children: <Widget>[ RaisedButton( onPressed: _increment, child: Text('Increment'), ), Text('Count: $_counter'), ], ); } } 可以看到 Flutter 中直接使用了和 React 中同名的setState方法,不过不会有变量合并的东西,当然也有生命周期。
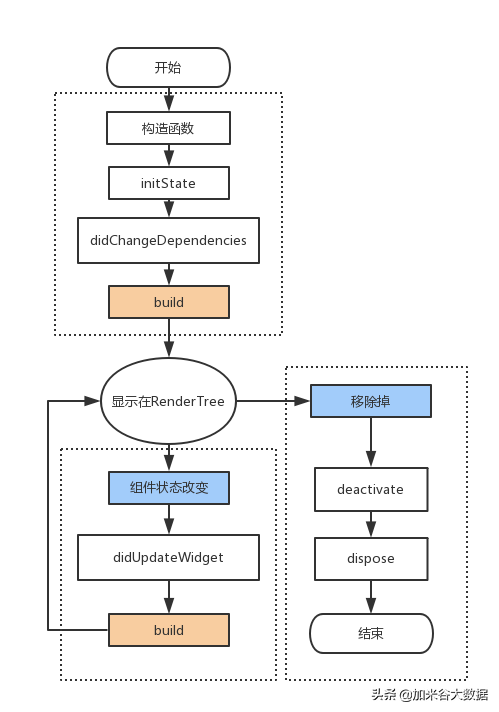
可以看到一个有状态的组件需要两个 Class,这样写的原因在于,Flutter 中 Widget 都是 immmutable 的,状态组件的状态保存在 State 中,组件仍然每次重新创建,Widget 在这里只是一种对组件的描述,Flutter 会 diff 转换成 Element,然后转换成 RenderObject 才渲染。
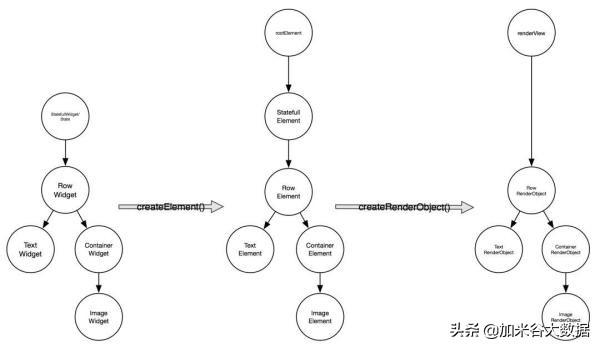
Flutter Widget 更多的渲染流程可以看这里。
实际上 Widget 只是作为组件结构一种描述,还可以带来的好处是,你可以更方便的做一些主题性的组件, Flutter 官方提供的Material Components widgets和Cupertino (iOS-style) widgets质量就相当高,再配合 Flutter 亚秒级的Hot Reload,开发体验可以说挺不错的。
State Management
setState()可以很方便的管理组件内的数据,但是 Flutter 中状态同样是从上往下流转的,因此也会遇到和 React 中同样的问题,如果组件树太深,逐层状态创建就显得很麻烦了,更不要说代码的易读和易维护性了。
InheritedWidget
同样 Flutter 也有个context一样的东西,那就是InheritedWidget,使用起来也很简单。
class GlobalData extends InheritedWidget { final int count; GlobalData({Key key, this.count,Widget child}):super(key:key,child:child); @override bool updateShouldNotify(GlobalData oldWidget) { return oldWidget.count != count; } static GlobalData of(BuildContext context) => context.inheritFromWidgetOfExactType(GlobalData); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { // This widget is the root of your application. @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'Flutter Demo', theme: ThemeData( primarySwatch: Colors.blue, ), home: MyHomePage(title: 'Flutter Demo Home Page'), ); } } class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget { MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key); final String title; @override _MyHomePageState createState() => _MyHomePageState(); } class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> { int _counter = 0; void _incrementCounter() { _counter++; }); } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text(widget.title), ), body: GlobalData( count: _counter, child: Center( child: Column( mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center, children: <Widget>[ Text( 'You have pushed the button this many times:', ), Text( '$_counter', style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.display1, ), Body(), Body2() ], ), ), ), floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton( onPressed: _incrementCounter, tooltip: 'Increment', child: Icon(Icons.add), ), ); } } class Body extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { GlobalData globalData = GlobalData.of(context); return Text(globalData.count.toString()); } } class Body2 extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { // TODO: implement build GlobalData globalData = GlobalData.of(context); return Text(globalData.count.toString()); } 具体实现原理可以参考这里,不过 Google 封装了一个更为上层的库provider,具体使用可以看这里。
BlOC
BlOC是 Flutter team 提出建议的另一种更高级的数据组织方式,也是我最中意的方式。简单来说:
Bloc = InheritedWidget + RxDart(Stream)
Dart 语言中内置了 Steam,Stream ~= Observable,配合RxDart, 然后加上StreamBuilder会是一种异常强大和自由的模式。
class GlobalData extends InheritedWidget { final int count; final Stream<String> timeInterval$ = new Stream.periodic(Duration(seconds: 10)).map((time) => new DateTime.now().toString()); GlobalData({Key key, this.count,Widget child}):super(key:key,child:child); @override bool updateShouldNotify(GlobalData oldWidget) { return oldWidget.count != count; } static GlobalData of(BuildContext context) => context.inheritFromWidgetOfExactType(GlobalData); } class TimerView extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { GlobalData globalData = GlobalData.of(context); return StreamBuilder( stream: globalData.timeInterval$, builder: (context, snapshot) { return Text(snapshot?.data ?? ''); } ); } } 当然 Bloc 的问题在于
- 学习成本略高,Rx 的概念要吃透,不然你会抓狂
- 自由带来的问题是,可能代码不如 Redux 类的规整。
顺便,今年 Apple 也拥抱了响应式,Combine(Rx like) + SwiftUI 也基本等于 Bloc 了。
所以,Rx 还是要赶紧学起来
除去 Bloc,Flutter 中还是可以使用其他的方案,譬如:
- Flutter Redux
- 阿里闲鱼的Fish Redux,据说性能很好。
- Mobx
- ……
展开来说现在的前端开发使用强大的框架页面组装已经不是难点了。开发的难点在于如何组合富交互所需的数据,也就是上面图中的state部分。
更具体来说,是怎么优雅,高效,易维护地处理短暂数据(ephemeral state)setState()和需要共享的 App State 的问题,这是个工程性的问题,但往往也是日常开发最难的事情了,引用 Redux 作者 Dan 的一句:
“The rule of thumb is:Do whatever is less awkward.”
到这里,主要的部分已经讲完了,有这些已经可以开发出一个不错的 App 了。剩下的就当成一个 bonus 吧。
测试
Flutter debugger,测试都是出场自带,用起来也不难。
// 测试在/test/目录下面 void main() { testWidgets('Counter increments smoke test', (WidgetTester tester) async { // Build our app and trigger a frame. await tester.pumpWidget(MyApp()); // Verify that our counter starts at 0. expect(find.text('0'), findsOneWidget); expect(find.text('1'), findsNothing); // Tap the '+' icon and trigger a frame. await tester.tap(find.byIcon(Icons.add)); await tester.pump(); // Verify that our counter has incremented. expect(find.text('0'), findsNothing); expect(find.text('1'), findsOneWidget); }); } 包管理,资源管理
类似与 JavaScript 的 npm,Flutter,也就是 Dart 也有自己的包仓库。不过项目包的依赖使用 yaml 文件来描述:
name: app description: A new Flutter project. version: 1.0.0+1 environment: sdk: ">=2.1.0 <3.0.0" dependencies: flutter: sdk: flutter cupertino_icons: ^0.1.2 生命周期
移动应用总归需要应用级别的生命周期,flutter 中使用生命周期钩子,也非常的简单:
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget { @override _MyAppState createState() => new _MyAppState(); } class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> with WidgetsBindingObserver { @override void initState() { super.initState(); WidgetsBinding.instance.addObserver(this); } @override void dispose() { WidgetsBinding.instance.removeObserver(this); super.dispose(); } @override void didChangeAppLifecycleState(AppLifecycleState state) { switch (state) { case AppLifecycleState.inactive: print('AppLifecycleState.inactive'); break; case AppLifecycleState.paused: print('AppLifecycleState.paused'); break; case AppLifecycleState.resumed: print('AppLifecycleState.resumed'); break; case AppLifecycleState.suspending: print('AppLifecycleState.suspending'); break; } super.didChangeAppLifecycleState(state); } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Container(); } } 使用原生能力
和 ReactNative 类似,Flutter 也是使用类似事件的机制来使用平台相关能力。
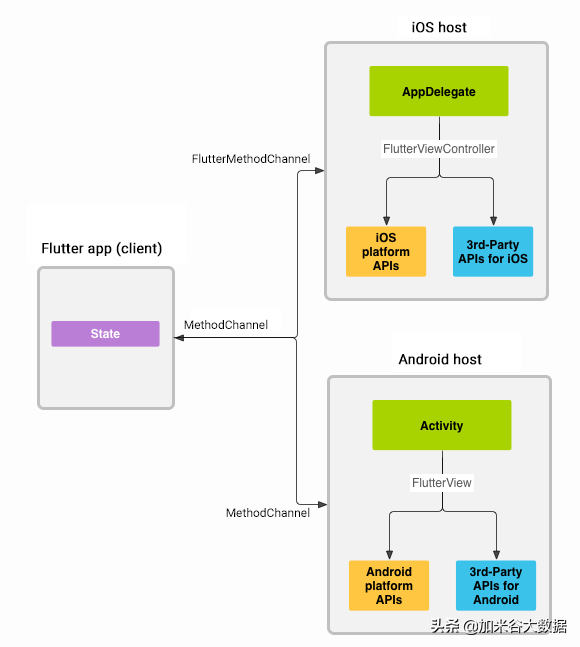
Flutter Web, Flutter Desktop
这些还在开发当中,鉴于对 Dart 喜欢,以及对 Flutter 性能的乐观,这些倒是很值得期待。
 鲁公网安备37020202000738号
鲁公网安备37020202000738号