Json有两种数据格式:前后台开发约定的一种数据格式,{key:value}类型的,key必须是字符串类型的,value是Object类型(也就是任意类型)
第一种: 对象格式{key:value}
第二种: 数组格式[{key:value,key1:value1},{key2:value2,key3:value3}]
注意:数组和对象格式可以相互嵌套的
比如:前端定义Json演示:
-------------------------------------------------------
定义的是对象格式的
-------------------------------------------------------
var person={"name":"张三丰","age":100,"gender":"男"};
// 取出名字和年龄
alert(person.name);
alert(person.age);
-------------------------------------------------------
定义的是数组格式的
-------------------------------------------------------
var persons=[
{"name":"张三丰","age":100,"gender":"男"},
{"name":"张太极","age":100,"gender":"男"}
];
// 取出张三丰
alert(persons[0].name);
// 取出张太极
alert(persons[1].name);
-------------------------------------------------------
对象格式和数组格式相互嵌套
-------------------------------------------------------
var json={ "weixiaobao":[
{"name":"建宁","age":26},
{"name":"阿珂","age":23},
{"name":"双儿","age":22}
],
"haohao":[
{"name":"建宁1","age":26},
{"name":"阿珂1","age":23},
{"name":"双儿1","age":22}
]
};
// 取出的是韦小宝下面的双儿
alert(json.weixiaobao[2].name);
// 取出的是好好下面的阿珂1
alert(json.haohao[1].name);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
后台定义
其实我一直后台开发过程中,被无数人说只要把Json格式的数据返回给前台就好了,我就一直很困惑,Json到底是啥,我怎么能把Json格式的数据传给前台呀,框架怎么处理Json的,案例演示:基于Maven的SpringMvc演示:
第一步:在前端控制器配置文件中添加支持Json的Bean
支持Json的Bean,配置ViewResolver。 可以用多个ViewResolver。 使用order属性排序。
InternalResourceViewResolver放在最后。
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.ContentNegotiatingViewResolver">
<property name="order" value="1" />
<property name="defaultViews">
<list>
<!-- JSON View -->
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.json.MappingJackson2JsonView">
</bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
第二步:在pom.xml文件中导入Json的依赖
<!-- 使用Json所依赖的jar包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
</dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
第三步:新建一个实体类(这是显示为Json数据的数据模型)
//注意:新建了一个包来装实体类 (getter和setter方法省略)
/**
* 用户实体类
*/
public class User {
private int id; //用户id
private String name; //用户姓名
private String sex; //性别
private List<String> hobby; //爱好
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
第四步:书写Controller中的生成Json数据的方法。
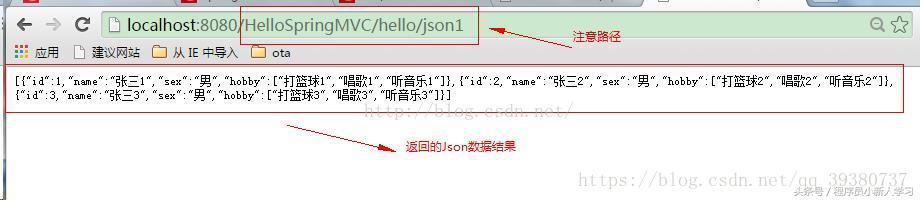
第一种:@ResponseBody通过注解来实现转成Json数据
/**
* 返回Json的示例:/hello/json1
*
* 这里加了@ResponseBody注解,说明将List<User>作为响应体,
* 将其响应为Json数据,因为已经在spring-mvc-servlet.xml进行配置
*
*/
@RequestMapping(value="json1",method=RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody List<User> getUserInJson1(){
//填充所需返回的数据,本来应该是查询数据库,这里就写假数据了,因为重点不是在这
List<User> list=new ArrayList<User>();
for(int i=1;i<=3;i++){
User user=new User();
user.setId(i);
user.setName("张三"+i);
user.setSex("男");
List<String> hobbies=new ArrayList<String>();
hobbies.add("打篮球"+i);
hobbies.add("唱歌"+i);
hobbies.add("听音乐"+i);
user.setHobby(hobbies);
list.add(user);
}
return list;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
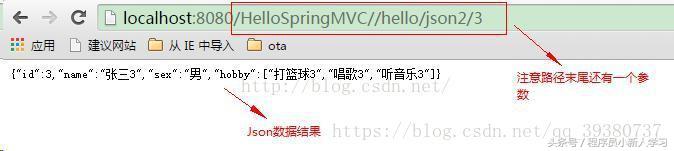
第二种:@PathVariable或@param注解实现转成Json数据
/**
* 返回Json的示例:/hello/json2/3
*
* 注意:路径后面的参数是user的id,这种写法是由@PathVariable这个注解决定的。
*
* 和写法1不同的是返回值没有注解了,变成了ResponseEntity<User>
*
* @param userId 需要查询的用户id
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value="/json2/{userId}",method=RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<User> getUserInJson2(@PathVariable Integer userId){
//填充所需返回的数据,本来应该是查询数据库。这里就写假数据了,因为重点不是在这
User user=new User();
user.setId(userId);
user.setName("张三"+userId);
user.setSex("男");
List<String> hobbies=new ArrayList<String>();
hobbies.add("打篮球"+userId);
hobbies.add("唱歌"+userId);
hobbies.add("听音乐"+userId);
user.setHobby(hobbies);
//这里也应该new 一个响应体,因为返回的是这种类型,第一个参数是需返回的实体类,第二个参数是状态码
//当然,也可返回一个List<User>类型,需更换为:return new ResponseEntity<List<User>>(list, HttpStatus.OK);
return new ResponseEntity<User>(user, HttpStatus.OK);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
运行结果:
方式一:
方式二:
 鲁公网安备37020202000738号
鲁公网安备37020202000738号