总感觉这个概念,和研发有点脱节;
一、基础概念
不同设备之间通过网络进行数据传输,并且基于通用的网络协议作为多种设备的兼容标准,称为网络通信;
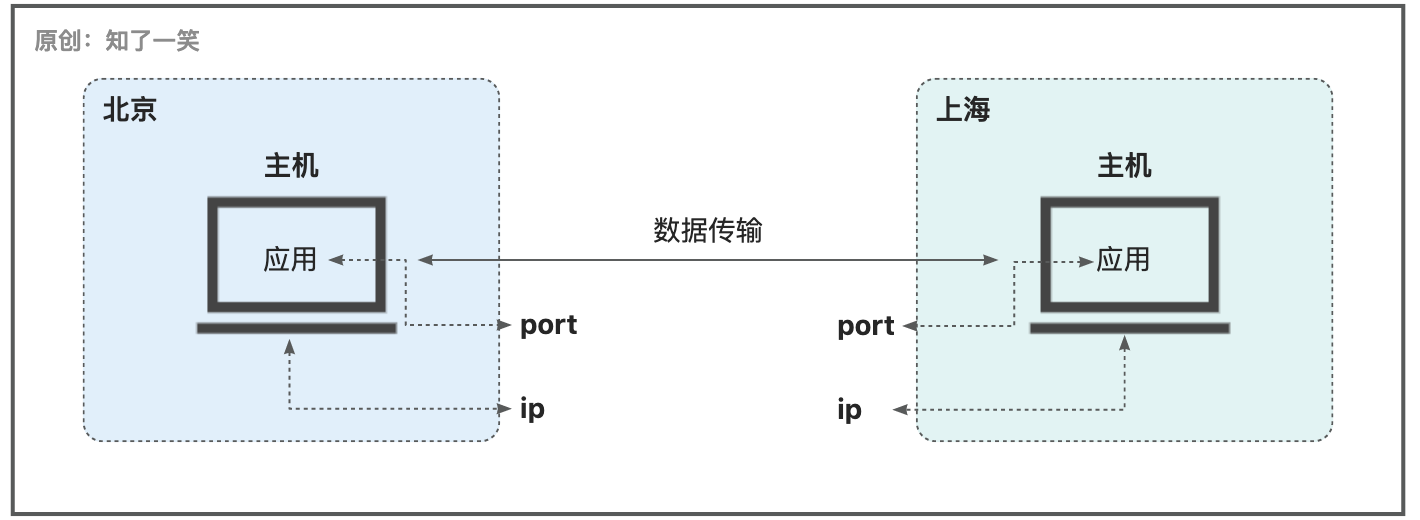
以C/S架构来看,在一次请求当中,客户端和服务端进行数据传输的交互时,在不同阶段和层次中需要遵守的网络通信协议也不一样;
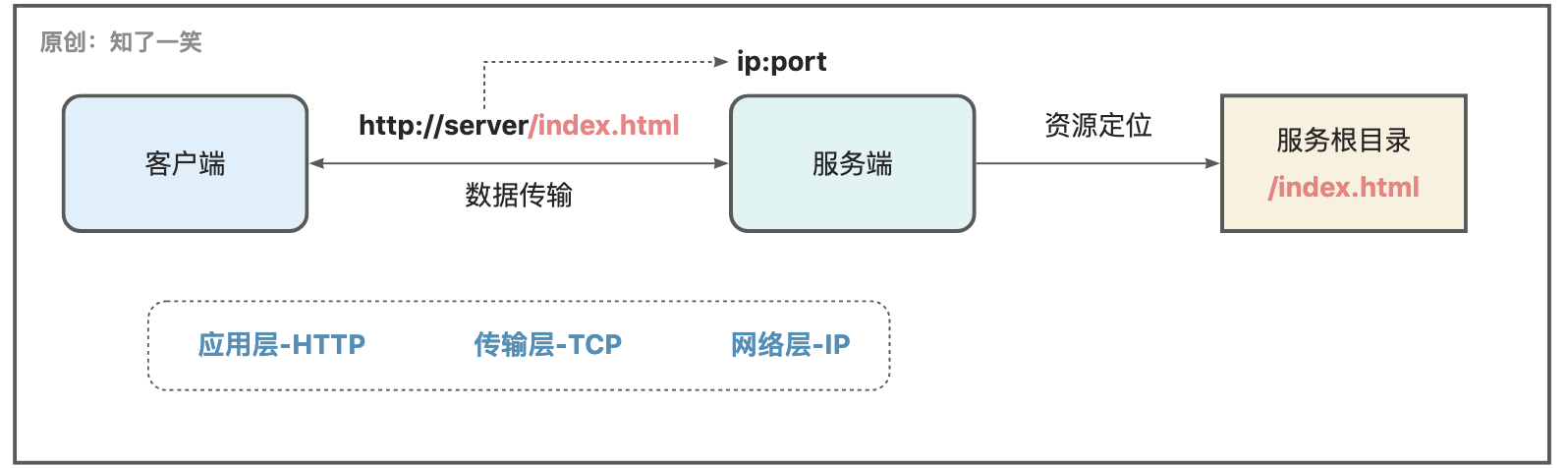
应用层:HTTP超文本传输协议,基于TCP/IP通信协议来传递数据;
传输层:TCP传输控制协议,采用三次握手的方式建立连接,形成数据传输通道;
网络层:IP协议,作用是把各种传输的数据包发送给请求的接收方;
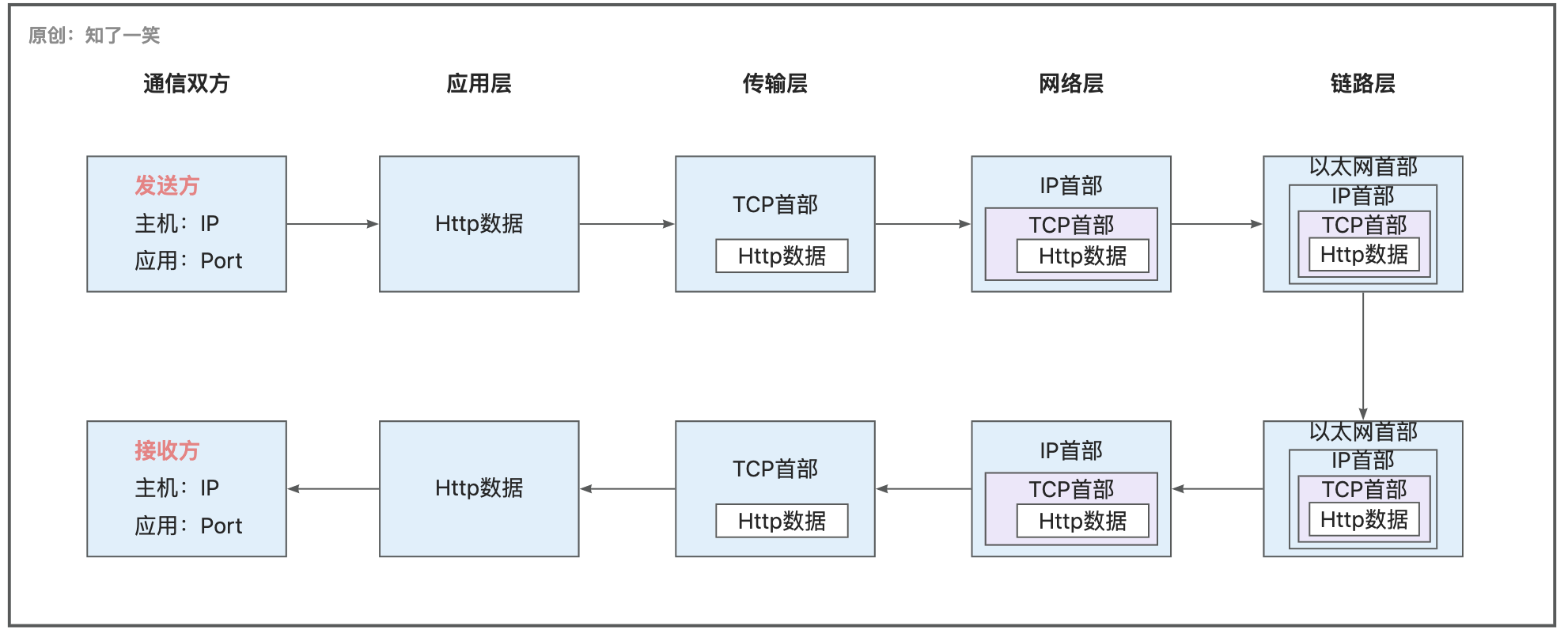
通信双方进行交互时,发送方数据在各层传输时,每通过一层就会添加该层的首部信息;接收方与之相反,每通过一次就会删除该层的首部信息;
二、JDK源码
在java.net源码包中,提供了与网络编程相关的基础API;
1、InetAddress
封装了对IP地址的相关操作,在使用该API之前可以先查看本机的hosts的映射,Linux系统中在/etc/hosts路径下;
import java.net.InetAddress;public class TestInet { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 获取本机 InetAddress 对象 InetAddress localHost = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); printInetAddress(localHost); // 获取指定域名 InetAddress 对象 InetAddress inetAddress = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com"); printInetAddress(inetAddress); // 获取本机配置 InetAddress 对象 InetAddress confAddress = InetAddress.getByName("nacos-service"); printInetAddress(confAddress); } public static void printInetAddress (InetAddress inetAddress){ System.out.println("InetAddress:"+inetAddress); System.out.println("主机名:"+inetAddress.getHostName()); System.out.println("IP地址:"+inetAddress.getHostAddress()); }}2、URL
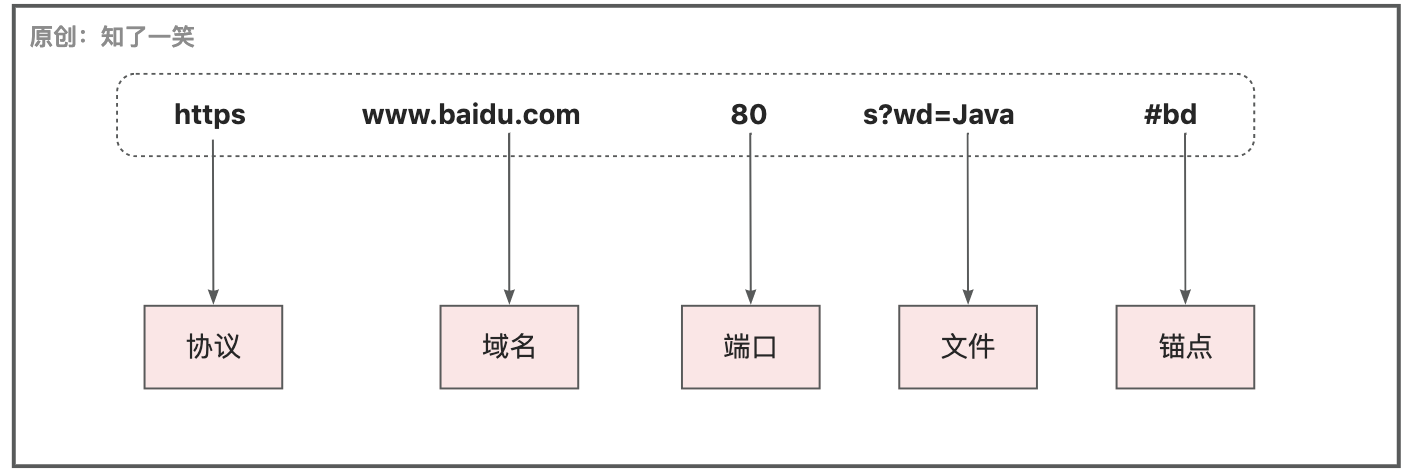
统一资源定位符,URL一般包括:协议、主机名、端口、路径、查询参数、锚点等,路径+查询参数,也被称为文件;
import java.net.URL;public class TestURL { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { URL url = new URL("https://www.baidu.com:80/s?wd=Java#bd") ; printURL(url); } private static void printURL (URL url){ System.out.println("协议:" + url.getProtocol()); System.out.println("域名:" + url.getHost()); System.out.println("端口:" + url.getPort()); System.out.println("路径:" + url.getPath()); System.out.println("参数:" + url.getQuery()); System.out.println("文件:" + url.getFile()); System.out.println("锚点:" + url.getRef()); }}3、HttpURLConnection
作为URLConnection的抽象子类,用来处理针对Http协议的请求,可以设置连接超时、读取超时、以及请求的其他属性,是服务间通信的常用方式;
public class TestHttp { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 访问 网址 内容 URL url = new URL("https://www.jd.com"); HttpURLConnection httpUrlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); printHttp(httpUrlConnection); // 请求 服务 接口 URL api = new URL("http://localhost:8082/info/99"); HttpURLConnection apiConnection = (HttpURLConnection) api.openConnection(); apiConnection.setRequestMethod("GET"); apiConnection.setConnectTimeout(3000); printHttp(apiConnection); } private static void printHttp (HttpURLConnection httpUrlConnection) throws Exception{ try (InputStream inputStream = httpUrlConnection.getInputStream()) { BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); String line ; while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(line); } } }}三、通信编程
1、Socket
Socket也被称为套接字,是两台设备之间通信的端点,会把网络连接当成流处理,则数据以IO形式传输,这种方式在当前被普遍采用;
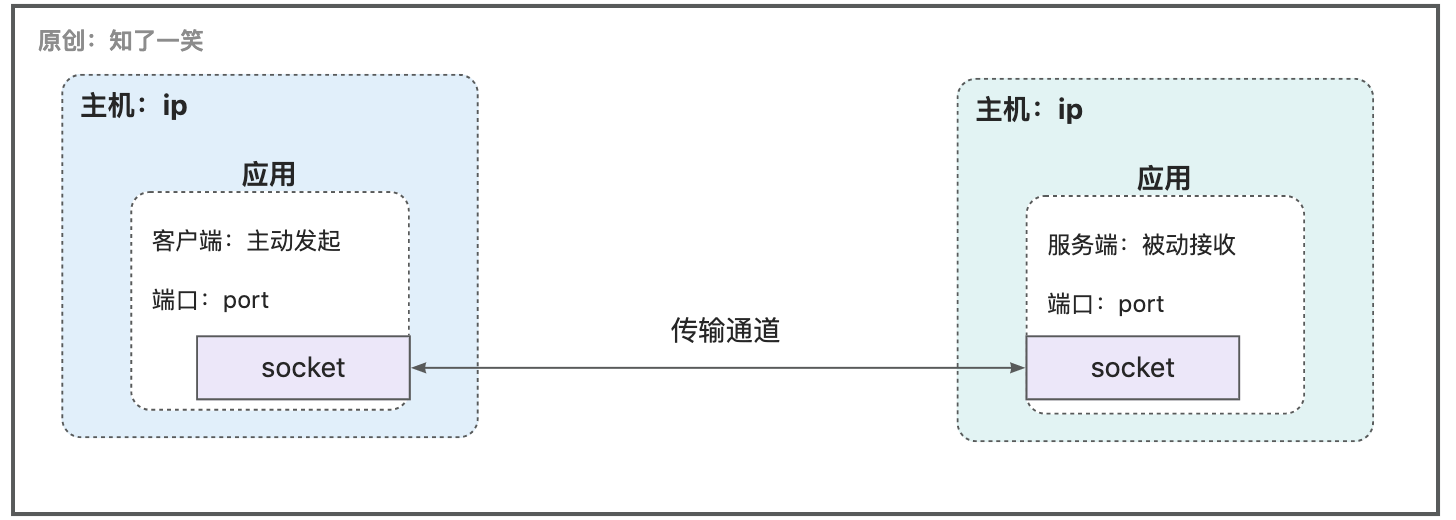
从网络编程直接跳到Socket套接字,概念上确实有较大跨度,概念过度抽象时,可以看看源码的核心结构,在理解时会轻松很多,在JDK中重点看SocketImpl抽象类;
public abstract class SocketImpl implements SocketOptions { // Socket对象,客户端和服务端 Socket socket = null; ServerSocket serverSocket = null; // 套接字的文件描述对象 protected FileDescriptor fd; // 套接字的路由IP地址 protected InetAddress address; // 套接字连接到的远程主机上的端口号 protected int port; // 套接字连接到的本地端口号 protected int localport;}套接字的抽象实现类,是实现套接字的所有类的公共超类,可以用于创建客户端和服务器套接字;
所以到底如何理解Socket概念?从抽象类中来看,套接字就是指代网络通讯中系统资源的核心标识,比如通讯方IP地址、端口、状态等;
2、SocketServer
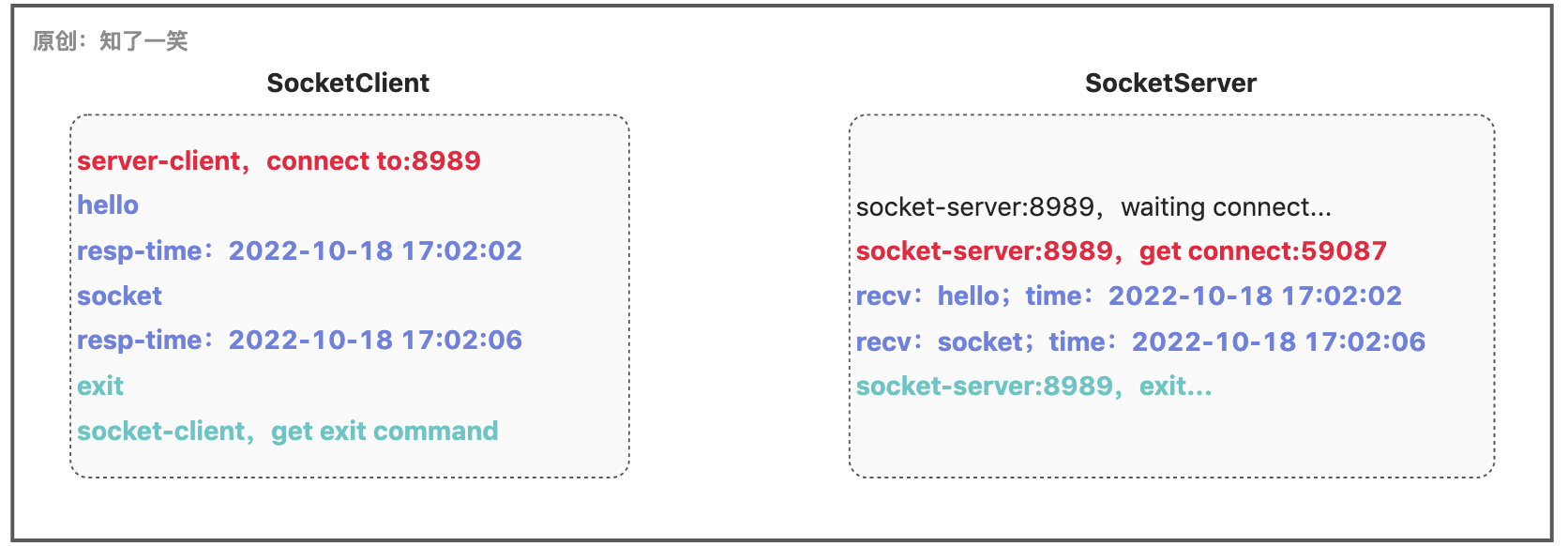
创建Socket服务端,并且在8989端口监听,接收客户端的连接请求和相关信息,并且响应客户端,发送指定的数据;
public class SocketServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 1、创建Socket服务端 ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8989); System.out.println("socket-server:8989,waiting connect..."); // 2、方法阻塞等待,直到有客户端连接 Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); System.out.println("socket-server:8989,get connect:"+socket.getPort()); // 3、输入流,输出流 InputStream inStream = socket.getInputStream(); OutputStream outStream = socket.getOutputStream(); // 4、数据接收和响应 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; int readLen = 0; while ((readLen=inStream.read(buf)) != -1){ // 接收数据 String readVar = new String(buf, 0, readLen) ; if ("exit".equals(readVar)){ break ; } System.out.println("recv:"+readVar+";time:"+DateTime.now().toString(DatePattern.NORM_DATETIME_PATTERN)); // 响应数据 outStream.write(("resp-time:"+DateTime.now().toString(DatePattern.NORM_DATETIME_PATTERN)).getBytes()); } // 5、资源关闭 outStream.close(); inStream.close(); socket.close(); serverSocket.close(); System.out.println("socket-server:8989,exit..."); }}需要注意的是步骤2输出的端口号是随机不确定的,结合jps和lsof -i tcp:port命令查看进程和端口号的占用情况;
3、SocketClient
创建Socket客户端,并且连接到服务端,读取命令行输入的内容并发送到服务端,并且输出服务端的响应数据;
public class SocketClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 1、创建Socket客户端 Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 8989); System.out.println("server-client,connect to:8989"); // 2、输入流,输出流 OutputStream outStream = socket.getOutputStream(); InputStream inStream = socket.getInputStream(); // 3、数据发送和响应接收 int readLen = 0; byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; while (true){ // 读取命令行输入 BufferedReader bufReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String iptLine = bufReader.readLine(); if ("exit".equals(iptLine)){ break; } // 发送数据 outStream.write(iptLine.getBytes()); // 接收数据 if ((readLen = inStream.read(buf)) != -1) { System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, readLen)); } } // 4、资源关闭 inStream.close(); outStream.close(); socket.close(); System.out.println("socket-client,get exit command"); }}测试结果:整个流程在没有收到客户端的exit退出指令前,会保持连接的状态,并且可以基于字节流模式,进行持续的数据传输;
4、字符流使用
基于上述的基础案例,采用字符流的方式进行数据传输,客户端和服务端只进行一次简单的交互;
-- 1、客户端BufferedReader bufReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inStream));BufferedWriter bufWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outStream));// 客户端发送数据bufWriter.write("hello,server");bufWriter.newLine();bufWriter.flush();// 客户端接收数据System.out.println("client-read:"+bufReader.readLine());-- 2、服务端BufferedReader bufReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inStream));BufferedWriter bufWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outStream));// 服务端接收数据System.out.println("server-read:"+bufReader.readLine());// 服务端响应数据bufWriter.write("hello,client");bufWriter.newLine();bufWriter.flush();5、文件传输
基于上述的基础案例,客户端向服务端发送图片文件,服务端完成文件的读取和保存,在处理完成后给客户端发送结果描述;
-- 1、客户端// 客户端发送图片FileInputStream fileStream = new FileInputStream("Local_File_Path/jvm.png");byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int i = 0;while ((i = fileStream.read(bytes)) != -1) { outStream.write(bytes);}// 写入结束标记,禁用此套接字的输出流,之后再使用输出流会抛异常socket.shutdownOutput();// 接收服务端响应结果System.out.println("server-resp:"+new String(bytes,0,readLen));-- 2、服务端// 接收客户端图片FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("Local_File_Path/new_jvm.png");byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int i = 0;while ((i = inStream.read(bytes)) != -1) { fileOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, i);}// 响应客户端文件处理结果outStream.write("file-save-success".getBytes());6、TCP协议
Socket网络编程是基于TCP协议的,TCP传输控制协议是一种面向连接的、可靠的、基于字节流的传输层通信协议,在上述案例中侧重基于流的数据传输,其中关于连接还涉及两个核心概念:
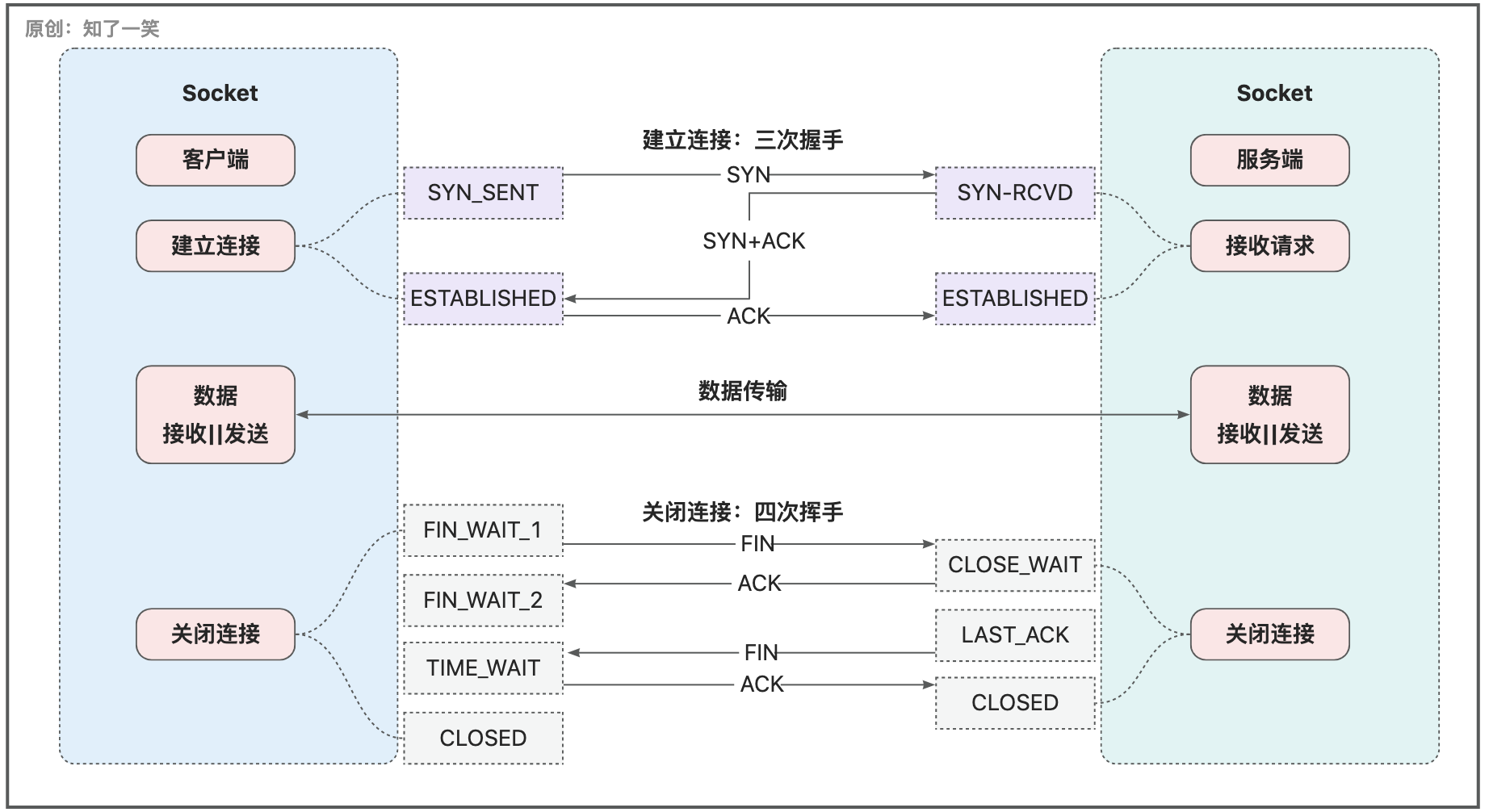
三次握手:建立连接的过程,在这个过程中进行了三次网络通信,当连接处于建立的状态,就可以进行正常的通信,即数据传输;四次挥手:关闭连接的过程,调用close方法,即连接使用结束,在这个过程中进行了四次网络通信;
四、Http组件
在服务通信时依赖网络,而对于编程来说,更常见的是的Http的组件,在微服务架构中,涉及到Http组件工具有很多,例如Spring框架中的RestTemplate,Feign框架支持ApacheHttp和OkHttp;下面围绕几个常用的组件编写测试案例;
1、基础接口
@RestControllerpublic class BizWeb { @GetMapping("/getApi/{id}") public Rep<Integer> getApi(@PathVariable Integer id){ log.info("id={}",id); return Rep.ok(id) ; } @GetMapping("/getApi_v2/{id}") public Rep<Integer> getApiV2(HttpServletRequest request, @PathVariable Integer id, @RequestParam("name") String name){ String token = request.getHeader("Token"); log.info("token={},id={},name={}",token,id,name); return Rep.ok(id) ; } @PostMapping("/postApi") public Rep<IdKey> postApi(HttpServletRequest request,@RequestBody IdKey idKey){ String token = request.getHeader("Token"); log.info("token={},idKey={}", token,JSONUtil.toJsonStr(idKey)); return Rep.ok(idKey) ; } @PutMapping("/putApi") public Rep<IdKey> putApi(@RequestBody IdKey idKey){ log.info("idKey={}", JSONUtil.toJsonStr(idKey)); return Rep.ok(idKey) ; } @DeleteMapping("/delApi/{id}") public Rep<Integer> delApi(@PathVariable Integer id){ log.info("id={}",id); return Rep.ok(id) ; }}2、ApacheHttp
public class TestApacheHttp { private static final String BASE_URL = "http://localhost:8083" ; public static void main(String[] args) { BasicHeader header = new BasicHeader("Token","ApacheSup") ; // 1、发送Get请求 Map<String,String> param = new HashMap<>() ; param.put("name","cicada") ; Rep getRep = doGet(BASE_URL+"/getApi_v2/3",header,param, Rep.class); System.out.println("get:"+getRep); // 2、发送Post请求 IdKey postBody = new IdKey(1,"id-key-我") ; Rep postRep = doPost (BASE_URL+"/postApi", header, postBody, Rep.class); System.out.println("post:"+postRep); } /** * 构建HttpClient对象 */ private static CloseableHttpClient buildHttpClient (){ // 请求配置 RequestConfig reqConfig = RequestConfig.custom().setConnectTimeout(6000).build(); return HttpClients.custom() .setDefaultRequestConfig(reqConfig).build(); } /** * 执行Get请求 */ public static <T> T doGet (String url, Header header, Map<String,String> param, Class<T> repClass) { // 创建Get请求 CloseableHttpClient httpClient = buildHttpClient(); HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(); httpGet.addHeader(header); try { URIBuilder builder = new URIBuilder(url); if (param != null) { for (String key : param.keySet()) { builder.addParameter(key, param.get(key)); } } httpGet.setURI(builder.build()); // 请求执行 HttpResponse httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet); if (httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) { // 结果转换 String resp = EntityUtils.toString(httpResponse.getEntity()); return JSONUtil.toBean(resp, repClass); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { IoUtil.close(httpClient); } return null; } /** * 执行Post请求 */ public static <T> T doPost (String url, Header header, Object body,Class<T> repClass) { // 创建Post请求 CloseableHttpClient httpClient = buildHttpClient(); HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url); httpPost.addHeader(header); StringEntity conBody = new StringEntity(JSONUtil.toJsonStr(body),ContentType.APPLICATION_JSON); httpPost.setEntity(conBody); try { // 请求执行 HttpResponse httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpPost); if (httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) { // 结果转换 String resp = EntityUtils.toString(httpResponse.getEntity()); return JSONUtil.toBean(resp, repClass); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { IoUtil.close(httpClient); } return null; }}3、OkHttp
public class TestOkHttp { private static final String BASE_URL = "http://localhost:8083" ; public static void main(String[] args) { Headers headers = new Headers.Builder().add("Token","OkHttpSup").build() ; // 1、发送Get请求 Rep getRep = execute(BASE_URL+"/getApi/1", Method.GET.name(), headers, null, Rep.class); System.out.println("get:"+getRep); // 2、发送Post请求 IdKey postBody = new IdKey(1,"id-key") ; Rep postRep = execute(BASE_URL+"/postApi", Method.POST.name(), headers, buildBody(postBody), Rep.class); System.out.println("post:"+postRep); // 3、发送Put请求 IdKey putBody = new IdKey(2,"key-id") ; Rep putRep = execute(BASE_URL+"/putApi", Method.PUT.name(), headers, buildBody(putBody), Rep.class); System.out.println("put:"+putRep); // 4、发送Delete请求 Rep delRep = execute(BASE_URL+"/delApi/2", Method.DELETE.name(), headers, null, Rep.class); System.out.println("del:"+delRep); } /** * 构建JSON请求体 */ public static RequestBody buildBody (Object body){ MediaType mediaType = MediaType.parse("application/json; charset=utf-8"); return RequestBody.create(mediaType, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(body)) ; } /** * 构建OkHttpClient对象 */ public static OkHttpClient buildOkHttp () { return new OkHttpClient.Builder() .readTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS).connectTimeout(6, TimeUnit.SECONDS) .connectionPool(new ConnectionPool(15, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) .build(); } /** * 执行请求 */ public static <T> T execute (String url, String method, Headers headers, RequestBody body, Class<T> repClass) { // 请求创建 OkHttpClient httpClient = buildOkHttp() ; Request.Builder requestBuild = new Request.Builder() .url(url).method(method, body); if (headers != null) { requestBuild.headers(headers); } try { // 请求执行 Response response = httpClient.newCall(requestBuild.build()).execute(); // 结果转换 InputStream inStream = null; if (response.isSuccessful()) { ResponseBody responseBody = response.body(); if (responseBody != null) { inStream = responseBody.byteStream(); } } if (inStream != null) { try { byte[] respByte = IoUtil.readBytes(inStream); if (respByte != null) { return JSONUtil.toBean(new String(respByte, Charset.defaultCharset()), repClass); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { IoUtil.close(inStream); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; }}4、RestTemplate
public class TestRestTemplate { private static final String BASE_URL = "http://localhost:8083" ; public static void main(String[] args) { RestTemplate restTemplate = buildRestTemplate() ; // 1、发送Get请求 Map<String,String> paramMap = new HashMap<>() ; Rep getRep = restTemplate.getForObject(BASE_URL+"/getApi/1",Rep.class,paramMap); System.out.println("get:"+getRep); // 2、发送Post请求 IdKey idKey = new IdKey(1,"id-key") ; Rep postRep = restTemplate.postForObject(BASE_URL+"/postApi",idKey,Rep.class); System.out.println("post:"+postRep); // 3、发送Put请求 IdKey idKey2 = new IdKey(2,"key-id") ; restTemplate.put(BASE_URL+"/putApi",idKey2,paramMap); // 4、发送Delete请求 restTemplate.delete(BASE_URL+"/delApi/2",paramMap); // 5、自定义Header请求 HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.add("Token","AdminSup"); HttpEntity<IdKey> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<>(idKey, headers); ResponseEntity<Rep> respEntity = restTemplate.exchange(BASE_URL+"/postApi", HttpMethod.POST, requestEntity, Rep.class); System.out.println("post-header:"+respEntity.getBody()); } private static RestTemplate buildRestTemplate (){ // 1、参数配置 SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory factory = new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory(); factory.setReadTimeout(3000); factory.setConnectTimeout(6000); // 2、创建对象 return new RestTemplate(factory) ; }}END



 鲁公网安备37020202000738号
鲁公网安备37020202000738号