有几个python模块可以让我们使用PostgreSQL连接和操作数据库:
- Psycopg2
- pg8000
- py-postgresql
- PyGreSQL
Psycopg2是PostgreSQL最受欢迎的python驱动程序之一。 它被积极维护并为不同版本的python提供支持。 它还提供对线程的支持,并且可以在多线程应用程序中使用。 由于这些原因,它是开发人员的流行选择。
在这一小节中,我们将通过在python中构建一个简单的数据库管理系统来探索使用psycopg2使用PostgreSQl的功能。
安装模块:
sudo pip3 install psycopg2 #使用的是 Ubuntu系统注意:如果您使用的是Python2,请使用pip install代替pip3,不过python2.7版本已经不再维护,不推荐使用。
在您的系统中安装了psycopg之后,我们可以连接到数据库并在Python中执行查询。
创建数据库
在我们可以使用python访问数据库之前,我们需要在postgresql中创建数据库。 要创建数据库,请遵循以下步骤:
1.登录PostgreSQL.
sudo -u postgres psql
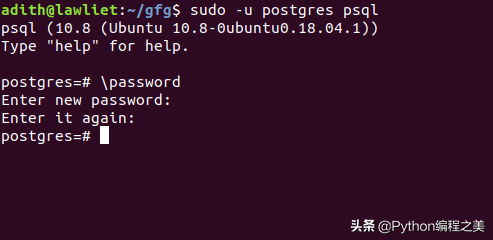
2.配置密码.
\password然后将提示您输入密码。 记住这一点,因为我们将使用它来连接到Python中的数据库。
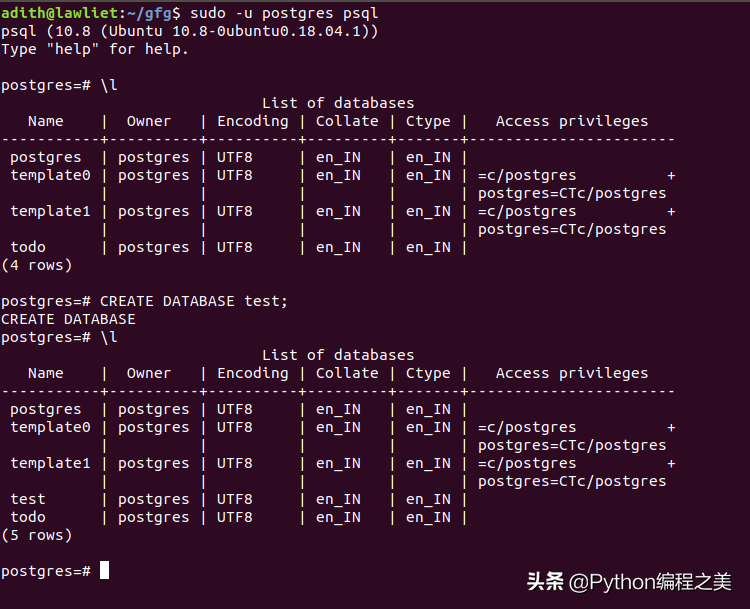
3.创建一个名为“ test”的数据库。 我们将连接到该数据库.
CREATE DATABASE test; #分号;别忘记带上配置数据库和密码后,退出psql服务器。
连接到数据库
connect()方法用于建立与数据库的连接。 它包含5个参数:
1.database:您要连接的数据库的名称
2.user:您本地系统的用户名
3.password:登录psql的密码
4.host:主机,默认情况下设置为localhost
5.port:端口号,默认为5432
conn = psycopg2.connect( database="test", user = "adith", password = "password", host = "localhost", port = "5432")建立连接后,我们可以使用python操作数据库。
Cursor对象用于执行sql查询。 我们可以使用连接对象(conn)创建一个游标对象
cur = conn.cursor() 使用此对象,我们可以更改连接到的数据库。
执行完所有查询后,我们需要断开连接。 不断开连接不会导致任何错误,但是通常认为断开连接是一种好习惯。
conn.close() 执行查询
execute()方法采用一个参数,即要执行的SQL查询。 SQL查询采用包含SQL语句的字符串形式。
cur.execute("SELECT * FROM emp") 获得数据
一旦执行了查询,就可以使用fetchall()方法获取查询的结果。 此方法不带参数,并返回选择查询的结果。
res = cur.fetchall() 查询结果存储在res变量中.
全部放在一起
在PostgreSQL中创建数据库后,就可以使用python访问该数据库。 我们首先使用以下模式在数据库中创建一个名为test的emp表:(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,名称VARCHAR(10),salary INT,dept INT)。 创建表后,没有任何错误,我们将值插入表中。
插入值后,我们可以查询表以选择所有行,并使用fetchall()函数将其显示给用户。
# importing libraries import psycopg2 # a function to connect to # the database. def connect(): # connecting to the database called test # using the connect function try: conn = psycopg2.connect(database ="test", user = "adith", password = "password", host = "localhost", port = "5432") # creating the cursor object cur = conn.cursor() except (Exception, psycopg2.DatabaseError) as error: print ("Error while creating PostgreSQL table", error) # returing the conn and cur # objects to be used later return conn, cur # a function to create the # emp table. def create_table(): # connect to the database. conn, cur = connect() try: # the test database contains a table called emp # the schema : (id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, # name VARCHAR(10), salary INT, dept INT) # create the emp table cur.execute('CREATE TABLE emp (id INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(10), salary INT, dept INT)') # the commit function permanently # saves the changes made to the database # the rollback() function can be used if # there are any undesirable changes and # it simply undoes the changes of the # previous query except: print('error') conn.commit() # a function to insert data # into the emp table def insert_data(id = 1, name = '', salary = 1000, dept = 1): conn, cur = connect() try: # inserting values into the emp table cur.execute('INSERT INTO emp VALUES(%s, %s, %s, %s)', (id, name, salary, dept)) except Exception as e: print('error', e) # commiting the transaction. conn.commit() # a function to fetch the data # from the table def fetch_data(): conn, cur = connect() # select all the rows from emp try: cur.execute('SELECT * FROM emp') except: print('error !') # store the result in data data = cur.fetchall() # return the result return data # a function to print the data def print_data(data): print('Query result: ') print() # iterating over all the # rows in the table for row in data: # printing the columns print('id: ', row[0]) print('name: ', row[1]) print('salary: ', row[2]) print('dept: ', row[3]) print('----------------------------------') # function to delete the table def delete_table(): conn, cur = connect() # delete the table try: cur.execute('DROP TABLE emp') except Exception as e: print('error', e) conn.commit() # driver function if __name__ == '__main__': # create the table create_table() # inserting some values insert_data(1, 'adith', 1000, 2) insert_data(2, 'tyrion', 100000, 2) insert_data(3, 'jon', 100, 3) insert_data(4, 'daenerys', 10000, 4) # getting all the rows data = fetch_data() # printing the rows print_data(data) # deleting the table # once we are done with # the program delete_table() 输出:

 鲁公网安备37020202000738号
鲁公网安备37020202000738号