在实际生活中,市场有这样的案例:写脚本来进行数据处理,比如说给数据库导入导出数据,这种任务一般来说最方便的方法是用python脚本,但是如果数据量比较大时候(比如上亿条)时候Python就会超级慢,看到无法忍受。在这种案例时候该怎么做呢,有一个外国老哥分享了自己的实践经历,并且对比了Python和Rust语言给SQLite插入十一条数据的情况,最后用Rust实现了在一分钟来完成任务。我们在此分享一下该实践过程,希望能对大家有所启迪,大家也可以尝试自己最拿手方法来实现该例子,并对比一下具体性能。

概述
案例中的任务是SQLite数据库插入10亿条的数据。表(user)数据结构和约束如下:
create table IF NOT EXISTS user
(
id INTEGER not null primary key,
area CHAR(6),
age INTEGER not null,
active INTEGER not null
);
随机生成数据。其中are列为六位数的区号(任何六位数字)。 age将是5、10 或15中的一个数字。Active为0或1。
实验环境硬件配置为:
MacBook Pro,2019(2.4 GHz 四核i5,8GB内存,256GB SSD硬盘,Big Sur 11.1)。
任务前提:
任务无需保持程序稳健性,如果进程崩溃并且所有数据都丢失了也没关系。可以再次运行脚本。
需要充分利用我的机器资源:100% CPU、8GB 内存和千兆字节的SSD空间。
无需使用真正的随机方法,stdlib伪随机方法即可。
Python原型
首先是原始版本的Python方法。Python标准库提供了一个SQLite模块,首先使用它编写了第一个版本。代码如下:
import sqlite3from commons import get_random_age, get_random_active, get_random_bool, get_random_area_code, create_tableDB_NAME = "naive.db"def faker(con: sqlite3.Connection, count=100_000):for _ in range(count):age = get_random_age()active = get_random_active()# switch for area codeif get_random_bool():# random 6 digit numberarea = get_random_area_code()con.execute('INSERT INTO user VALUES (NULL,?,?,?)', (area, age, active))else:con.execute('INSERT INTO user VALUES (NULL,NULL,?,?)', (age, active))con.commit()def main():con = sqlite3.connect(DB_NAME, isolation_level=None)con.execute('PRAGMA journal_mode = WAL;')create_table(con)faker(con, count=10_000_000)if __name__ == '__main__':main()
在该脚本中,通for循环中一一插入1000万条数据。执行花了将近15分钟。基于此进行优化迭代,提高性能。
SQLite中,每次插入都是原子性的并且为一个事务。每个事务都需要保证写入磁盘(涉及IO操作),因此可能会很慢。为了优化,可以尝试通过不同大小的批量插入,对比发现,100000是最佳选择。通过这个简单的更改,运行时间减少到了10分钟,优化了3分之一,但是仍然非常耗时。优化后,批量插入版本源码:
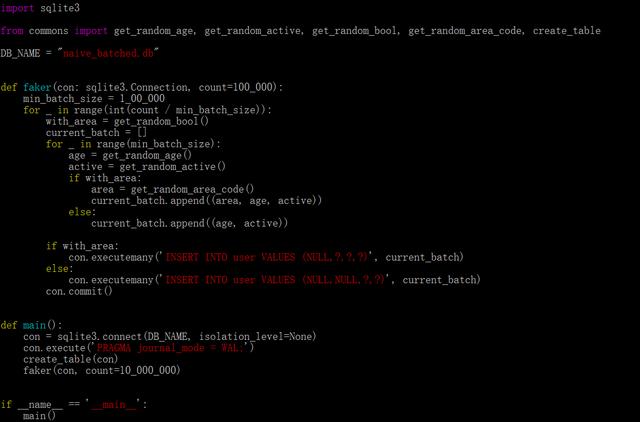
SQLite库优化
除了在代码层优化外,如果对于单纯的数据写入,对数据库本身搞的优化也是非常重要的。对于SQLite优化,可以做如下配置:
PRAGMA journal_mode = OFF;PRAGMA synchronous = 0;PRAGMA cache_size = 1000000;PRAGMA locking_mode = EXCLUSIVE;PRAGMA temp_store = MEMORY;具体解释:
首先,journal_mode设置为OFF,将会关闭回滚日志,禁用 SQLite 的原子提交和回滚功能,这样在事务失败情况下,无法恢复,基于例子实例稳健性要求可以设置,但是严禁在生产环境中使用。
其次,关闭synchronous,SQLite这可以不再校验磁盘写入的数据可靠性。写入SQLite可能并不意味着它已刷新到磁盘。同样,严禁在生产环境中启用。
cache_size用户指定SQLite允许在内存中保留多少内存页。不要在生产中分配太高的的数值。
使用在EXCLUSIVE锁定模式,SQLite连接持有的锁永远不会被释放。
设置temp_store到MEMOR将使其表现得像一个内存数据库。
优化性能
对上面的两个脚本,添加 SQLite优化参数,然后重新运行:
def main(): con = sqlite3.connect(DB_NAME, isolation_level=None) con.execute('PRAGMA journal_mode = OFF;') con.execute('PRAGMA synchronous = 0;') con.execute('PRAGMA cache_size = 1000000;') # give it a GB con.execute('PRAGMA locking_mode = EXCLUSIVE;') con.execute('PRAGMA temp_store = MEMORY;') create_table(con) faker(con, count=100_000_000)优化后版本,原始版本,插入1亿行数据,大概花了10分钟;对比批量插入版本大概花了8.5分钟。
pypy版本
对比CPython PyPy在数据处理中可以提高性能,据说可以提高4倍以上的性能。本实验中也尝试编译PyPy解释器,运行脚本(代码无需修改)。
使用pypy解释器,批处理版本,插入1亿行数据只需2.5分钟。性能大概是Cpython的3.5倍,可见传说的4倍性能提高确实是真的,诚不我欺也!。同时,为了测试在纯循环插入中消耗的时间,在脚本中删除SQL指令并运行:
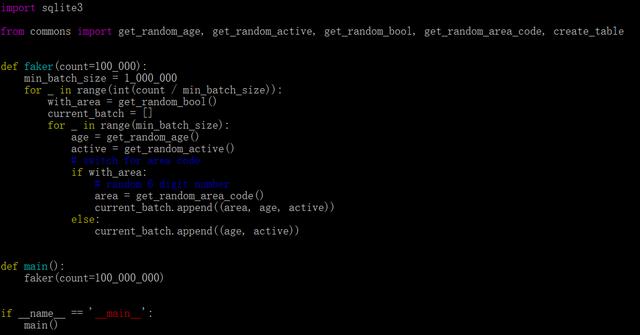
以上脚本在CPython 中耗时5.5分钟 。PyPy执行耗时1.5分钟(同样提高了3.5倍)。
Rust
在完成Python各种优化折腾有。又尝试了Rust版本的插入,对比也有个原始版本和批量插入版本。原始版本,也是每行插入:
use rusqlite::{params, Connection};mod common;fn faker(mut conn: Connection, count: i64) {let tx = conn.transaction().unwrap();for _ in 0..count {let with_area = common::get_random_bool();let age = common::get_random_age();let is_active = common::get_random_active();if with_area {let area_code = common::get_random_area_code();tx.execute("INSERT INTO user VALUES (NULL, ?, ?, ?)",params![area_code, age, is_active],).unwrap();} else {tx.execute("INSERT INTO user VALUES (NULL, NULL, ?, ?)",params![age, is_active],).unwrap();}}tx.commit().unwrap();}fn main() {let conn = Connection::open("basic.db").unwrap();conn.execute_batch("PRAGMA journal_mode = OFF;PRAGMA synchronous = 0;PRAGMA cache_size = 1000000;PRAGMA locking_mode = EXCLUSIVE;PRAGMA temp_store = MEMORY;",).expect("PRAGMA");conn.execute("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user (id INTEGER not null primary key,area CHAR(6),age INTEGER not null,active INTEGER not null)",[],).unwrap();faker(conn, 100_000_000)}该版执行,大概用时3分钟。 然后我做了进一步的实验:
将rusqlite,换成sqlx异步运行。
use std::str::FromStr;use sqlx::sqlite::{SqliteConnectOptions, SqliteJournalMode, SqliteSynchronous};use sqlx::{ConnectOptions, Connection, Executor, SqliteConnection, Statement};mod common;async fn faker(mut conn: SqliteConnection, count: i64) -> Result<(), sqlx::Error> { let mut tx = conn.begin().await?; let stmt_with_area = tx .prepare("INSERT INTO user VALUES (NULL, ?, ?, ?)") .await?; let stmt = tx .prepare("INSERT INTO user VALUES (NULL, NULL, ?, ?)") .await?; for _ in 0..count { let with_area = common::get_random_bool(); let age = common::get_random_age(); let is_active = common::get_random_active(); if with_area { let area_code = common::get_random_area_code(); stmt_with_area .query() .bind(area_code) .bind(age) .bind(is_active) .execute(&mut tx) .await?; } else { stmt.query() .bind(age) .bind(is_active) .execute(&mut tx) .await?; } } tx.commit().await?; Ok(())}#[tokio::main]async fn main() -> Result<(), sqlx::Error> { let mut conn = SqliteConnectOptions::from_str("basic_async.db") .unwrap() .create_if_missing(true) .journal_mode(SqliteJournalMode::Off) .synchronous(SqliteSynchronous::Off) .connect() .await?; conn.execute("PRAGMA cache_size = 1000000;").await?; conn.execute("PRAGMA locking_mode = EXCLUSIVE;").await?; conn.execute("PRAGMA temp_store = MEMORY;").await?; conn.execute( "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user ( id INTEGER not null primary key, area CHAR(6), age INTEGER not null, active INTEGER not null);", ) .await?; faker(conn, 100_000_000).await?; Ok(())}这个版本花了大约14分钟。性能反而下降下降了。比Python版本还要差(原因值得深析)。
对执行的原始SQL语句,切换到准备好的语句并在循环中插入行,但重用了准备好的语句。该版本只用了大约一分钟。
使用准备好的语句并将它们插入到50行的批次中,插入10亿条,耗时34.3 秒。
use rusqlite::{Connection, ToSql, Transaction};mod common;fn faker_wrapper(mut conn: Connection, count: i64) {let tx = conn.transaction().unwrap();faker(&tx, count);tx.commit().unwrap();}fn faker(tx: &Transaction, count: i64) {// that is, we will batch 50 inserts of rows at oncelet min_batch_size: i64 = 50;if count < min_batch_size {panic!("count cant be less than min batch size");}// jeez, refactor this!let mut with_area_params = " (NULL, ?, ?, ?),".repeat(min_batch_size as usize);with_area_params.pop();let with_area_params = with_area_params.as_str();let mut without_area_params = " (NULL, NULL, ?, ?),".repeat(min_batch_size as usize);without_area_params.pop();let without_area_params = without_area_params.as_str();let st1 = format!("INSERT INTO user VALUES {}", with_area_params);let st2 = format!("INSERT INTO user VALUES {}", without_area_params);let mut stmt_with_area = tx.prepare_cached(st1.as_str()).unwrap();let mut stmt = tx.prepare_cached(st2.as_str()).unwrap();for _ in 0..(count / min_batch_size) {let with_area = common::get_random_bool();let age = common::get_random_age();let is_active = common::get_random_active();let mut param_values: Vec<_> = Vec::new();if with_area {// lets prepare the batchlet mut vector = Vec::<(String, i8, i8)>::new();for _ in 0..min_batch_size {let area_code = common::get_random_area_code();vector.push((area_code, age, is_active));}for batch in vector.iter() {param_values.push(&batch.0 as &dyn ToSql);param_values.push(&batch.1 as &dyn ToSql);param_values.push(&batch.2 as &dyn ToSql);}stmt_with_area.execute(&*param_values).unwrap();} else {// lets prepare the batchlet mut vector = Vec::<(i8, i8)>::new();for _ in 0..min_batch_size {vector.push((age, is_active));}for batch in vector.iter() {param_values.push(&batch.0 as &dyn ToSql);param_values.push(&batch.1 as &dyn ToSql);}stmt.execute(&*param_values).unwrap();}}}fn main() {let conn = Connection::open("basic_batched.db").unwrap();conn.execute_batch("PRAGMA journal_mode = OFF;PRAGMA synchronous = 0;PRAGMA cache_size = 1000000;PRAGMA locking_mode = EXCLUSIVE;PRAGMA temp_store = MEMORY;",).expect("PRAGMA");conn.execute("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user (id INTEGER not null primary key,area CHAR(6),age INTEGER not null,active INTEGER not null)",[],).unwrap();faker_wrapper(conn, 100_000_000)}创建了一个线程版本,其中有一个从通道接收数据的写入线程和四个将数据推送到管道其他线程。
use rusqlite::{Connection, ToSql};use std::sync::mpsc;use std::sync::mpsc::{Receiver, Sender};use std::thread;mod common;static MIN_BATCH_SIZE: i64 = 50;enum ParamValues {WithArea(Vec<(String, i8, i8)>),WithoutArea(Vec<(i8, i8)>),}fn consumer(rx: Receiver<ParamValues>) {let mut conn = Connection::open("threaded_batched.db").unwrap();conn.execute_batch("PRAGMA journal_mode = OFF;PRAGMA synchronous = 0;PRAGMA cache_size = 1000000;PRAGMA locking_mode = EXCLUSIVE;PRAGMA temp_store = MEMORY;",).expect("PRAGMA");conn.execute("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user (id INTEGER not null primary key,area CHAR(6),age INTEGER not null,active INTEGER not null)",[],).unwrap();let tx = conn.transaction().unwrap();{// jeez, refactor this!let mut with_area_params = " (NULL, ?, ?, ?),".repeat(MIN_BATCH_SIZE as usize);with_area_params.pop();let with_area_params = with_area_params.as_str();let mut without_area_params = " (NULL, NULL, ?, ?),".repeat(MIN_BATCH_SIZE as usize);without_area_params.pop();let without_area_params = without_area_params.as_str();let st1 = format!("INSERT INTO user VALUES {}", with_area_params);let st2 = format!("INSERT INTO user VALUES {}", without_area_params);let mut stmt_with_area = tx.prepare_cached(st1.as_str()).unwrap();let mut stmt_without_area = tx.prepare_cached(st2.as_str()).unwrap();for param_values in rx {let mut row_values: Vec<&dyn ToSql> = Vec::new();match param_values {ParamValues::WithArea(values) => {for batch in values.iter() {row_values.push(&batch.0 as &dyn ToSql);row_values.push(&batch.1 as &dyn ToSql);row_values.push(&batch.2 as &dyn ToSql);}stmt_with_area.execute(&*row_values).unwrap();}ParamValues::WithoutArea(values) => {for batch in values.iter() {row_values.push(&batch.0 as &dyn ToSql);row_values.push(&batch.1 as &dyn ToSql);}stmt_without_area.execute(&*row_values).unwrap();}}}}tx.commit().unwrap();}fn producer(tx: Sender<ParamValues>, count: i64) {if count < MIN_BATCH_SIZE {panic!("count cant be less than min batch size");}for _ in 0..(count / MIN_BATCH_SIZE) {let with_area = common::get_random_bool();let age = common::get_random_age();let is_active = common::get_random_active();let mut param_values: Vec<_> = Vec::new();if with_area {// lets prepare the batchlet mut vector = Vec::<(String, i8, i8)>::new();for _ in 0..MIN_BATCH_SIZE {let area_code = common::get_random_area_code();vector.push((area_code, age, is_active));}for batch in vector.iter() {param_values.push(&batch.0 as &dyn ToSql);param_values.push(&batch.1 as &dyn ToSql);param_values.push(&batch.2 as &dyn ToSql);}// send the valuestx.send(ParamValues::WithArea(vector)).unwrap();} else {// lets prepare the batchlet mut vector = Vec::<(i8, i8)>::new();for _ in 0..MIN_BATCH_SIZE {vector.push((age, is_active));}for batch in vector.iter() {param_values.push(&batch.0 as &dyn ToSql);param_values.push(&batch.1 as &dyn ToSql);}// send the valuestx.send(ParamValues::WithoutArea(vector)).unwrap();}}}fn main() {// setup the DB and tableslet (tx, rx): (Sender<ParamValues>, Receiver<ParamValues>) = mpsc::channel();// lets launch the consumerlet consumer_handle = thread::spawn(|| consumer(rx));let cpu_count = num_cpus::get();let total_rows = 100_000_000;let each_producer_count = (total_rows / cpu_count) as i64;let mut handles = Vec::with_capacity(cpu_count);for _ in 0..cpu_count {let thread_tx = tx.clone();handles.push(thread::spawn(move || {producer(thread_tx, each_producer_count.clone())}))}for t in handles {t.join().unwrap();}drop(tx);// wait till consumer is exitedconsumer_handle.join().unwrap();}这是性能最好的版本,耗时约32.37秒。
基准测试对比
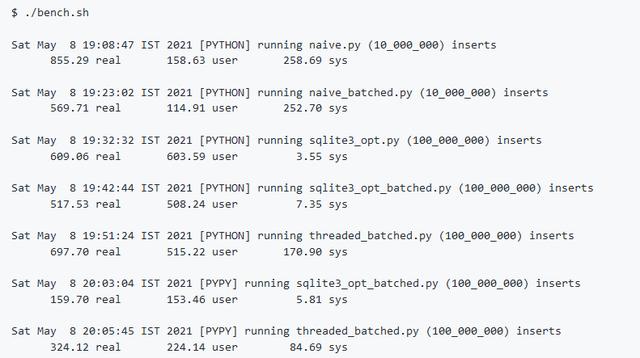
总结
通过案例不同任务实验,总体上可以得到:
通过SQLite PRAGMA语句优化设置可以提高插入性能。
使用准备好的语句可以提高性能
进行批量插入可以提高性能。
PyPy 实际上比CPython快4倍
线程/异步不一定能提高性能。
 鲁公网安备37020202000738号
鲁公网安备37020202000738号